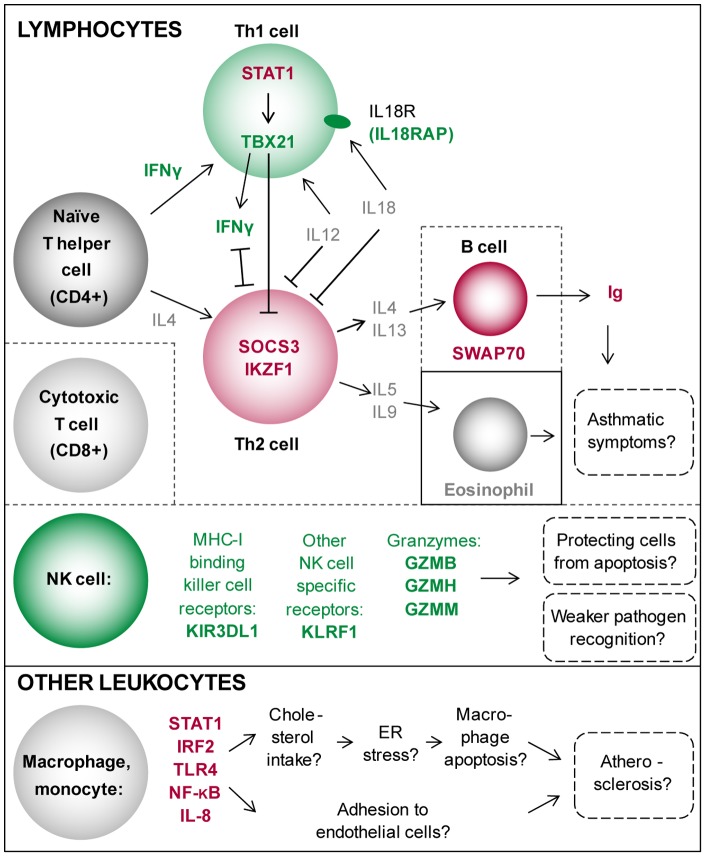
Figure 3. Differentiation and activation of lymphocyte and other leukocyte populations in cumulative sleep restriction (SR).
Arrows (↑) illustrate activating and blunt ended lines (T) inhibiting effects. Red = increased after SR, green = decreased after SR, grey = no change observed. IFNγ = interferon γ, IL = interleukin, STAT1, TBX21 and SOCS3 = transcription factors, Ig = immunoglobulins. (The factors involved in T helper (Th) cell differentiation modified after [30]). We propose that cumulative SR via the activation of B cell-mediated humoral immunity by Th2 cells may lead to increased risk for development or exacerbation of asthmatic symptoms. We also suggest that SR may participate in the development of atherosclerosis through increased cholesterol intake into macrophages. On the other hand, the reduction in the NK cell type immune response may be a mode to protect the self from destruction by apoptosis and/or might contribute to the attenuated immune response towards pathogens.