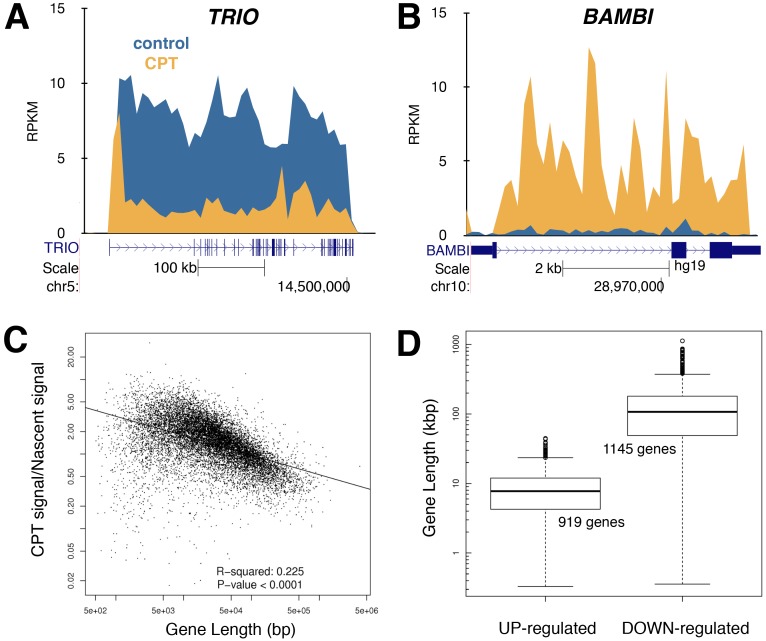
Figure 1. Gene size is a major contributing factor to the effects of camptothecin on RNA synthesis.
Human fibroblasts were treated with 20 µM camptothecin for 45 min with 2 mM Bru added during the last 15 min of camptothecin treatment to label nascent RNA followed by Bru-Seq. (A), Long genes, such as TRIO, exhibit elongation defects, but not transcription initiation, after camptothecin treatment. (B), Short genes, such as BAMBI, show a relative increase of RNA synthesis following camptothecin treatment. (C), Effect of camptothecin on relative transcription as a function of gene size. Ratio of Bru-Seq signal of individual genes in camptothecin-treated over control cells as a function of gene size. Longer genes are inhibited preferentially over shorter genes. (D), The median length of genes induced >2-fold by camptothecin (919 genes) is 8,927 bp, whereas genes down-regulated >2-fold (1,145 genes) have a median length of 136,355 bp. The gene maps are from RefSeq Genes (UCSC genome browser).