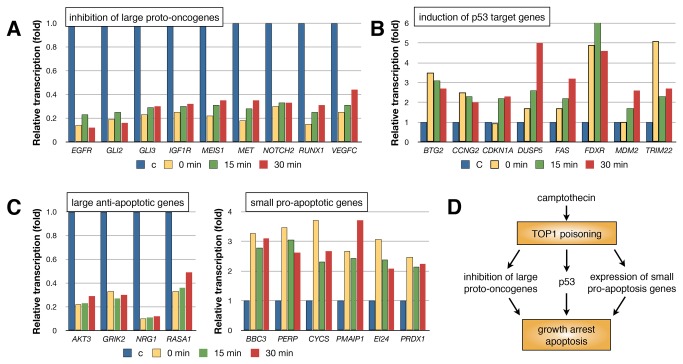
Figure 6. Camptothecin preferentially inhibits large genes such as proto-oncogenes and anti-apoptotic genes, enhances the relative expression of small pro-apoptotic genes and activates the p53 response.
(A), Examples of large proto-oncogenes inhibited by camptothecin and showing no recovery (or slow recovery) following drug removal. (B), Examples of p53 target genes induced following camptothecin treatment. (C), Examples of large anti-apoptotic genes showing reduced relative transcription (left) and examples of small pro-apoptotic genes showing enhanced relative transcription following camptothecin treatment (right). (D), Model of mechanisms by which camptothecin may induce cell death or inhibit cell growth. Camptothecin triggers a p53 transcriptional response and selectively inhibits large proto-oncogenes and survival genes. The data is color coded where blue represents control (C), yellow represents 15 min Bru-labeling at the end of a 45 min camptothecin treatment with no recovery (“0 min”), green represents drug washout and 15 min Bru-labeling immediately after washout (“15 min”) and finally red represents labeling 15-30 minutes following washout (“30 min”).