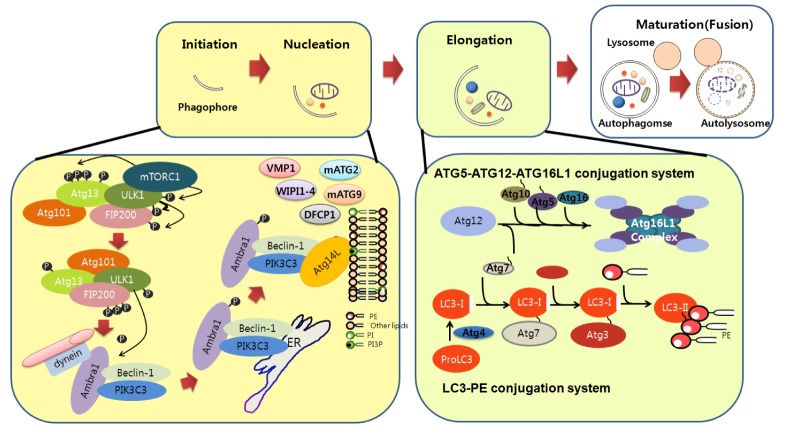
Fig. 1.
Molecular components and signaling of autophagy. Autophagy begins with phagophore formation (isolation membrane). Initiation of phagophore formation is tightly regulated by various protein complexes. Under nutrient conditions, mTOR in the mTORC complex interacts with the ULK complex, thereby limiting its activity. mTOR is inhibited by autophagy induction conditon such as starvation, thereby activating the ULK complex, which in turn activates and translocates the PIK3C3 complex from microtubules to the ER. Beclin1, together with other components of the PIK3C3 complex such as Atg14, promotes PIK3C3 kinase activity. Activated PIK3C3 kinase generates PI3P, which in turn recruits WIPI1-4, VMP1, DFCP1, mATG2, and transmembrane mATG9 to nucleate the phagophore in close proximity to the cargo. Elongation of the phagophore to the limiting membrane around the cargo is regulated by the ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L1 and LC3-PE conjugation systems. ATG12 binds to ATG5, followed by ATG16L1 binding to form the ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L1 complex. LC3-PE complex formation is initiated by cleavage of LC3 by ATG4, followed by coordinated interactions with the ATG7, ATG3 (an E2 ligase), and ATG5-ATG12-ATG16L1 complex to generate LC3-PE on the phagophore membranes. The autophagosome then directly fuses with lysosomes for final degradation.