Figure 6.
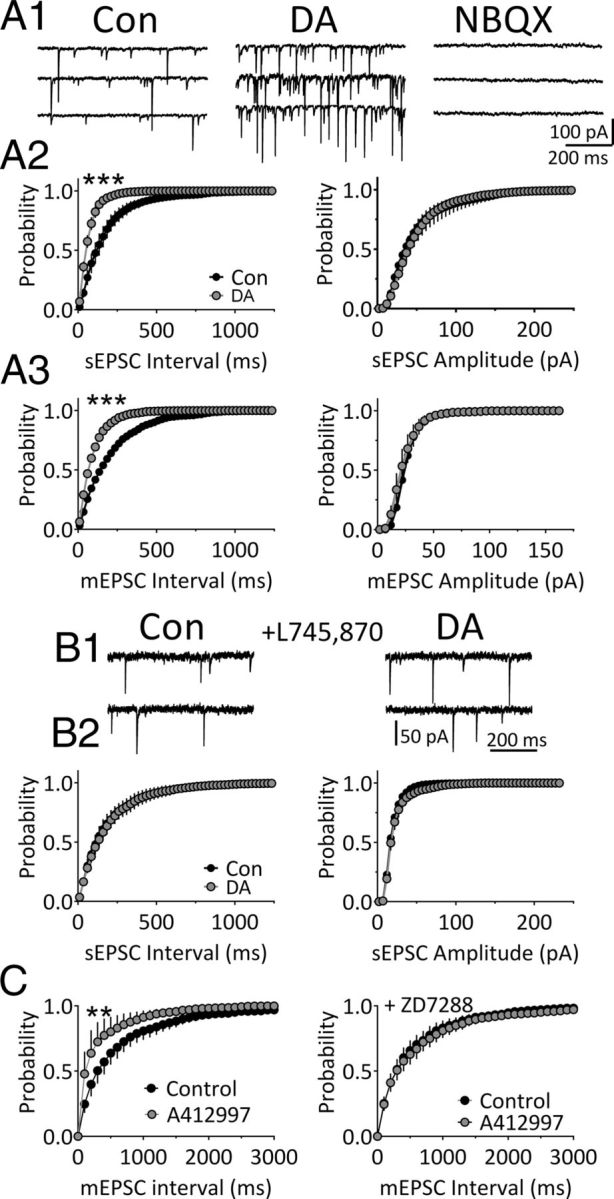
DA increases quantal glutamate release via D4Rs in mLHb neurons. A1, Traces showing sEPSCs recorded during baseline (Con) and during application of DA (3 μm) in an mLHb neuron. The AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist NBQX (10 μm) completely blocked the sEPSCs, indicating that they were mediated by glutamate receptors. A2, Mean cumulative probability histograms showing the effect of DA on sEPSC frequency (interval) and amplitude in mLHb neurons (n = 6). A3, Mean cumulative probability histograms showing the effects of DA on mEPSC frequency and amplitude in LHb neurons preincubated in TTX (1 μm). sEPSC and mEPSC intervals were significantly shortened (i.e., frequencies were increased) by DA (***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, KS test). B1, Traces of sEPSCs recorded during baseline and DA application following preincubation in the DA D4R antagonist L745,870 (200 nm). B2, Mean cumulative probability histograms showing the lack of effect of DA on sEPSC frequency (interval) and amplitude in mLHb neurons preincubated in L745,870 (n = 6). C, The selective D4R agonist A412997 (1 μm) increases the frequency of mEPSCs (left, n = 8), and this is blocked by ZD7288 (50 μm; right, n = 9), suggesting that D4Rs increase glutamate release via augmentation of Ih in axon terminals.
