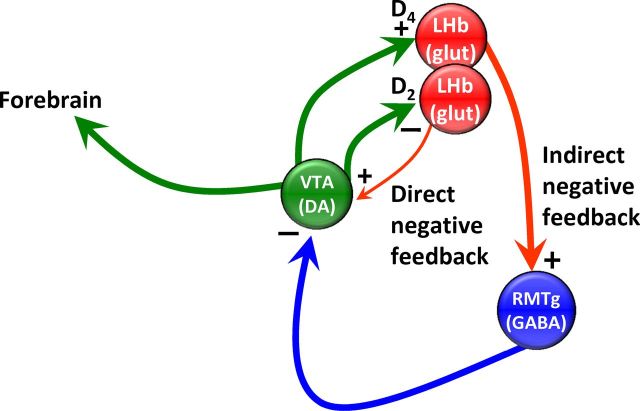
Figure 9.
Hypothesized direct and indirect inhibitory feedback pathways from the LHb to midbrain DA neurons distinguished by D4 or D2 receptor control. In the direct negative feedback pathway D2Rs on LHb glutamatergic neurons are activated by DA release from midbrain DA neurons. D2Rs inhibit these LHb neurons, thereby decreasing glutamate release onto midbrain DA neurons, causing inhibition. In the indirect negative feedback pathway, DA release onto D4Rs excites LHb neurons via the following three mechanisms; increased Ih; increased glutamate release; and decreased GABA release. The LHb neurons depolarized by D4R activation project to the GABAergic output neurons of the RMTg, increasing their excitability, thereby strongly inhibiting midbrain DA neurons via GABA release from RMTg cells. In both cases, the net effect is the inhibition of DA neuron activity following initial activation. However, the indirect pathway may have a larger influence on midbrain DA neurons because the LHb projection to RMTg is larger than the direct projection from the LHb to the midbrain.