Figure 2.
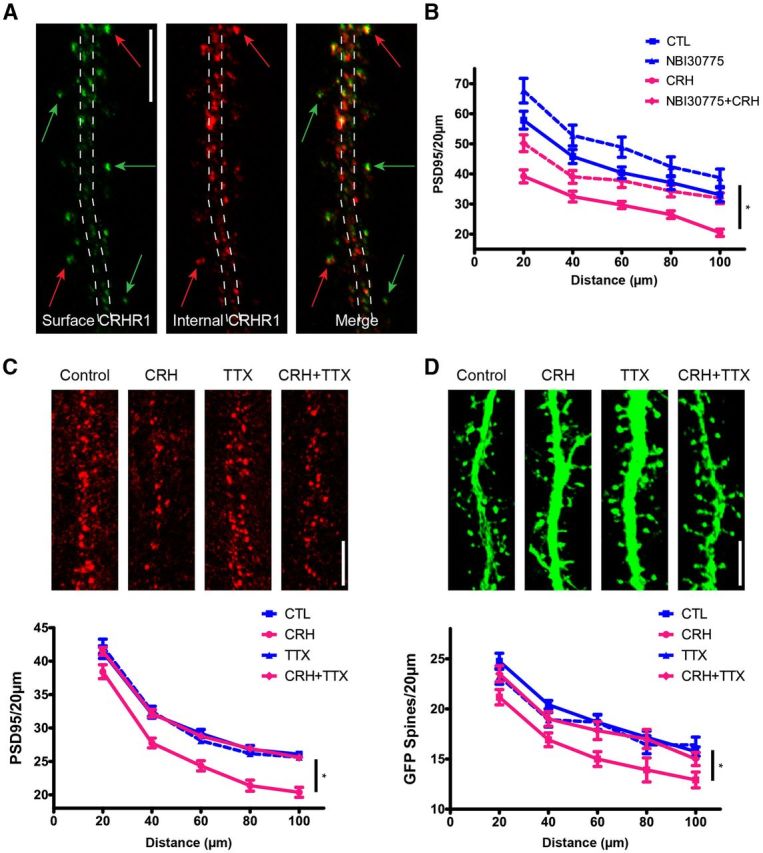
CRH-induced spine loss involves CRHR1. Cultured hippocampal neurons express CRHR1. Nonpermeable and permeabilized ICC conditions discriminate surface versus internal pools of CRHR1. A, Surface CRHR1 (green) was immunolabeled under nonpermeable conditions. After permeabilization, the neuron was processed for ICC for internal CRHR1 (red). The dashed lines approximate the contour of the dendrite. Green arrows point to surface CRHR1, the majority of which are located away from the dendrite and likely on dendritic spines. Red arrows point to external CRHR1 away from the dendritic shaft that colocalize with internal pools of CRHR1. These colocalized puncta are likely spines carrying the external receptor within the postsynaptic density as well as internal pools of CRHR1. B, Graph depicting that the CRHR1-selective antagonist (NBI30775; 100 nm) prevents CRH-induced loss of PSD95 puncta (p > 0.05; n = 12). C, D, CRH-induced spine loss requires neuronal activity. In the presence of TTX, CRH no longer reduces PSD95 puncta (F(3,368) = 20.31, p < 0.001; n = 12; C) or GFP-filled spines (F(3,176) = 6.29, p = 0.001; n = 12; D). Scale bars: A, C, D, 5 μm.
