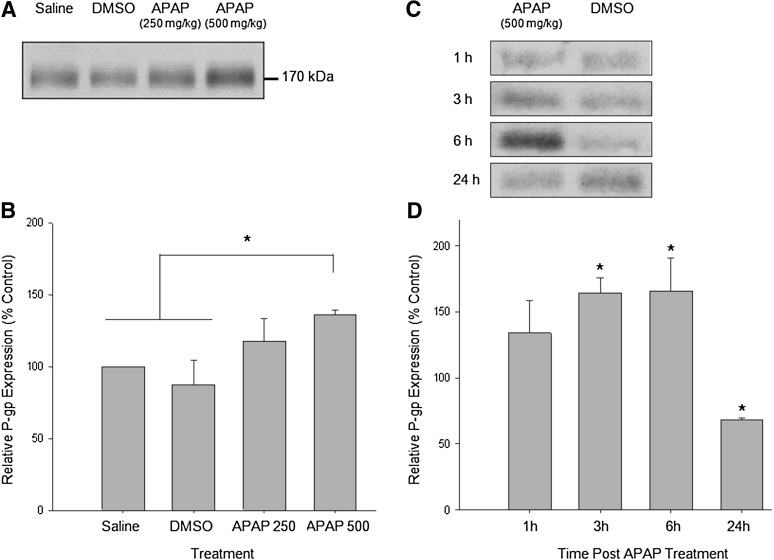
Fig. 1.
APAP increases P-gp protein expression in a concentration-dependent manner. (A) Animals were administered (i.p.) a single injection of saline, DMSO (vehicle control), APAP 250 mg/kg, or APAP 500 mg/kg. After 3 hours, animals were sacrificed and brain microvessels were isolated and prepared for Western blot analysis. Whole microvessels (10 μg) were resolved on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. Samples were analyzed for expression of P-gp. (B) Relative levels of P-gp expression in samples from A were determined by densitometric analysis. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of three separate experiments (nine animals per group). Asterisks represent data points that are significantly different from control (*P < 0.05). (C) Animals were administered (i.p.) a single injection of DMSO or APAP 500 mg/kg. After 1, 3, 6, or 24 hours, animals were sacrificed and brain microvessels were isolated and prepared for Western blot analysis. Whole microvessels (10 μg) were resolved on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane. Samples were analyzed for expression of P-gp. (D) Relative levels of P-gp expression in samples from C were determined by densitometric analysis. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of three separate experiments (nine animals per group). Asterisks represent data points that are significantly different from control (*P < 0.05).