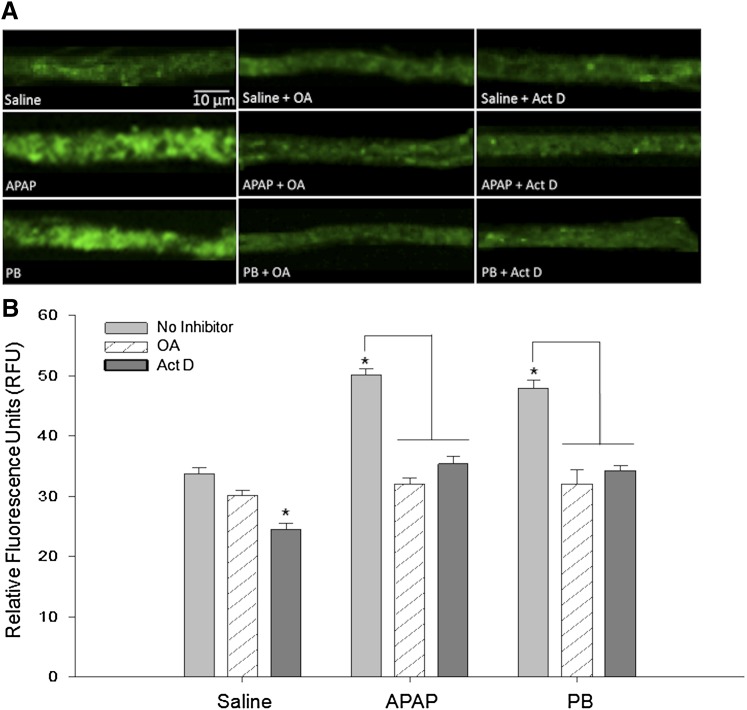
Fig. 6.
APAP-induced increase in P-gp transport attenuated by protein phosphatase 2A/CAR pathway inhibitor OA and transcriptional inhibitor/CAR pathway inhibitor Act D. Animals were administered (i.p.) a single injection of OA or Act D 1 hour prior to administration of saline, APAP (500 mg/kg), or PB (80 mg/kg). After 3 hours, animals were sacrificed and brain microvessels were isolated and prepared for ex vivo transport assay. Scale bar = 10 μm. (A) Representative confocal images show decreased luminal accumulation of BODIPY-verapamil, an established P-gp substrate, following treatment with PP2A inhibitor OA or transcriptional inhibitor Act D. (B) Quantification of luminal fluorescence shows that APAP- and PB-induced increases in P-gp transport activity are attenuated by OA and Act D pretreatment. Results are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of at least 50 individual capillaries per group from two separate experiments. Asterisks represent data points that are significantly different from saline, unless otherwise indicated (*P < 0.05).