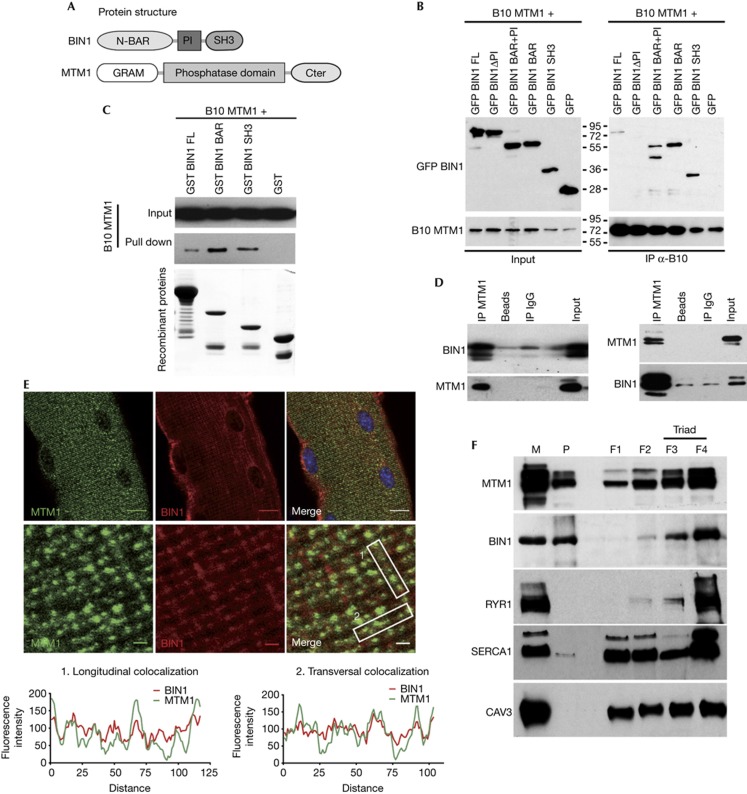
Figure 1.
MTM1 and BIN1 interact in vitro and in vivo and partially colocalize in skeletal muscle. (A) Representation of domains of BIN1 (isoform 8) and MTM1 proteins. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation assays using anti-B10 antibodies on lysates from COS-1 cells expressing B10-MTM1 and GFP-fused BIN1 domains. Top panel: immunoblot hybridized with anti-GFP antibodies. Bottom panel: immunoblot hybridized with anti-MTM1 antibodies. (C) MTM1 and BIN1 interact directly. GST (negative control), GST-BIN1, GST-BAR and GST-SH3 recombinant proteins were used to pull down B10-MTM1 produced by in vitro translation. Top panels: immunoblot hybridized with anti-B10 antibody. Bottom panel: Coomassie blue staining showing recombinant proteins used for the pull-down. (D) BIN1 and MTM1 interact in vivo. Co-immunoprecipitation assays on membrane-enriched fractions from mouse muscle homogenates using anti-MTM1 (left panel) or anti-BIN1 (right panel) antibodies. Immunoblots were hybridized with anti-BIN1 or anti-MTM1 antibodies. Non-conjugated beads and IgG were used as controls. (E) MTM1 and BIN1 partially localize on the same subcellular structure in isolated muscle fibres. Muscle fibres isolated from 5-week-old wild-type mouse were stained with anti-MTM1 and pan-isoform anti-BIN1 antibodies. Confocal planes in the middle of fibres. Scale bar, 10 μm (top panel), 1 μm (middle panel). Quantitative measurement of BIN1 and MTM1 fluorescence intensity (bottom panel). (F) MTM1 and BIN1 are both enriched at the triads. Subcellular fractionation of membranes from rabbit skeletal muscle on the basis of a discontinuous sucrose gradient, as in Amoasii et al [7]. Longitudinal sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes were enriched in fractions F1 and F2 (SERCA1), and triad membranes were enriched in fractions F3 and F4 (RYR1). Caveolin-3 was used as a sarcolemmal marker. BAR, BIN/Amphiphysin/Rvs; BIN1, amphiphysin 2; GFP, green fluorescent protein; GST, glutathione S-transferase; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitation; M, microsome; MTM1, myotubularin; P, pellet.