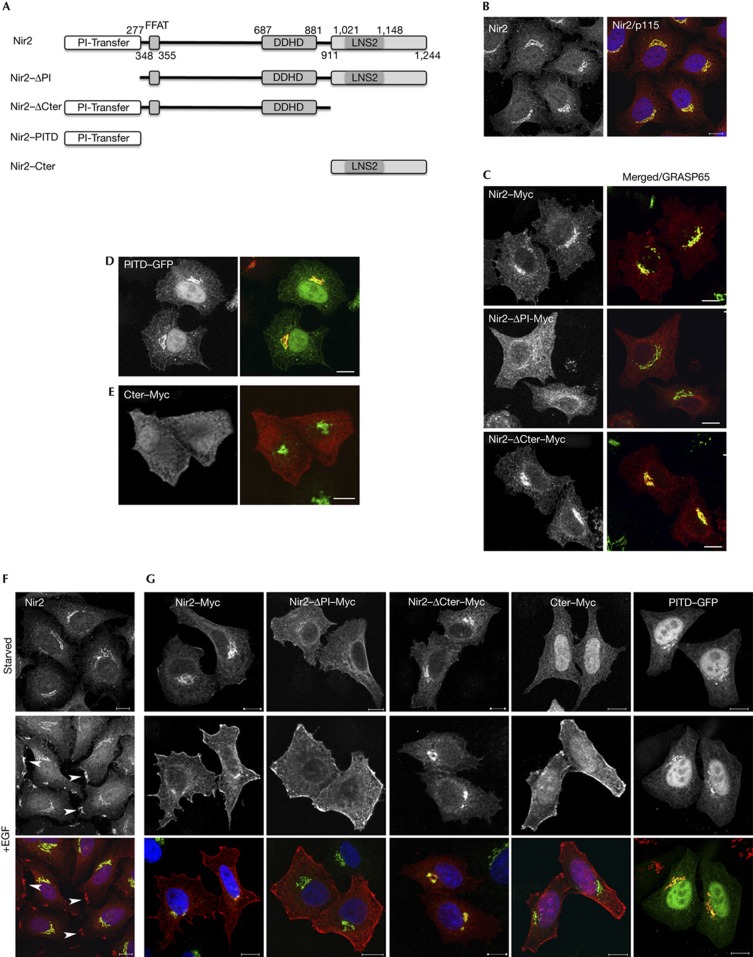
Figure 1.
The PITD is essential for the Golgi localization of Nir2, whereas the C-terminal region mediates its PM targeting. (A) Domain organization of Nir2 and its truncated mutants. The N-terminal PITD, the FFAT motif that mediates its interaction with VAP-A/B proteins, the DDHD domain and the C-terminal region containing the LNS2 (Lipin/Nde1/Smp2) domain. (B) Endogenous Nir2 (red) is localized mainly to the Golgi apparatus of HeLa cells as shown by its co-localization with the Golgi marker p115 (green). (C–E) The Golgi localization of Myc-tagged Nir2 protein and its indicated mutants was assessed by colocalization with the indicated Golgi markers (p115 and GRASP65) in HeLa cells. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F,G) The localization of endogenous Nir2 (F) or ectopically expressed Myc-tagged Nir2 and its indicated truncated mutants (G) in serum-starved or EGF-treated (10 min, 100 ng/ml) HeLa cells was examined by double immunostaining with anti-Nir2 (F) or anti-Myc (G) antibodies (red) together with anti-p115 antibody (green). Localizations at PM patches are marked by arrowheads (F). Scale bar, 10 μm. EGF, epidermal growth factor; GFP, green fluorescent protein; PITD, phosphatidylinositol-transfer domain; PM, plasma membrane.