Fig 8.
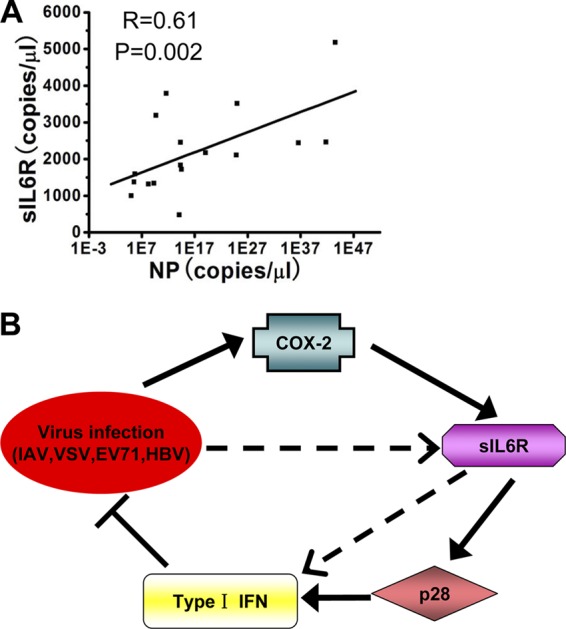
(A) The relative sIL6R and viral NP levels in throat swab samples were subjected to correlation analysis (n = 23). (B) Hypothetical model for COX-2-mediated sIL6R expression. Solid arrows represent signaling pathways identified in this study. Broken arrows indicate potential signaling pathways. Viruses (IAV, VSV, EV71, and HBV) induce sIL6R expression through the COX-2 pathway. The enhanced sIL6R activates type I IFN expression through the p28 pathway, leading to the activation of downstream effectors and the inhibition of viral replication. In addition, there are other potential signaling pathways that may regulate sIL6R-mediated antiviral function.
