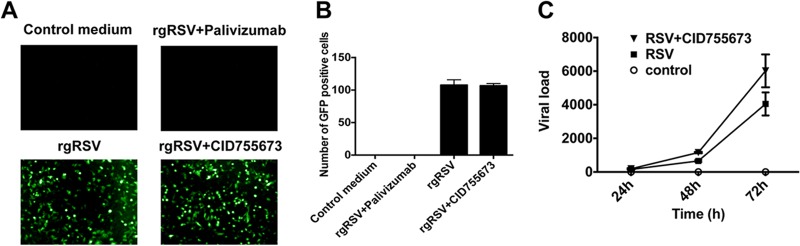
Fig 8.
PKD inhibitor did not inhibit early RSV infection or viral replication in epithelial cells. Polarized epithelial cells were preincubated with PKD inhibitor for 2 h, followed by infection with rgRSV at an MOI of 0.05 to 0.5, and rinsed twice with PBS after 2 h, followed by incubation at 37°C for 16 h. Palivizumab, a monoclonal antibody against RSV fusion (F) protein, was used as a positive control, which was also added 2 h before RSV infection. Sixteen hours post-RSV infection, live cells were subjected to fluorescence microscopy. (A and B) GFP+ cells are readily apparent after rgRSV infection, which was completely inhibited using pavilizumab. In contrast, the PKD inhibitor did not affect the number of GFP+ cells. A representative example (A, lower right) and averages of 3 experiments (B) are shown. (C) In parallel, inhibition of PKD did not affect RSV replication, as determined in cells infected with RSV A2 and by RT-PCR with primers that amplify the RSV A2 F protein. The images are representative of 3 independent experiments. The data are representative of three experiments (n = 3 per experiment). The error bars indicate SEM.