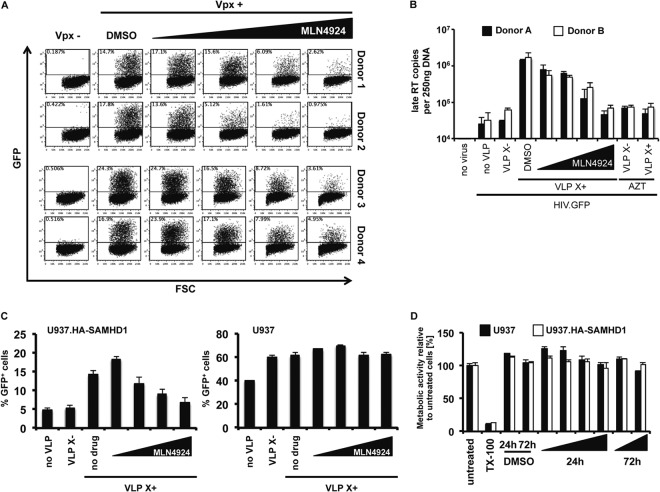
Fig 1.
MLN4924 inhibits Vpx function in cells that express SAMHD1. (A) MLN4924 (0.05, 0.25, 1.0, or 2.0 μM) or DMSO was added to cultures of MDDC isolated from four donors. The cells were infected with Vpx-containing or control HIV.GFP reporter virus, and after 3 days, the number of infected cells was quantified by flow cytometry. The data shown are representative of three experiments. FSC, forward scatter. (B) MLN4924 was added to MDDC from two donors at the same concentrations as listed in the legend to panel A. The cells were infected with an HIV.GFP reporter virus, and after 24 h, DNA was isolated. Newly synthesized late reverse transcripts were quantified by qRT-PCR using the DNA as the template. To control for contaminating plasmid DNA, a control was included in which AZT was added 14 h prior to infection. VLP X−, VLP lacking Vpx; VLP X+, VLP containing Vpx. (C) MLN4924 was added, as described in the legend to panel A, to PMA-differentiated U937-HA.SAMHD1 or parental U937 cells. After 2 h, Vpx-containing or control VLP were added and the cells were infected with an HIV.GFP reporter virus. After 3 days, the number of infected cells was quantified by flow cytometry. The results shown are the averages of triplicate infections. (D) Differentiated U937 and U937.HA-SAMHD1 cells were incubated with increasing amounts of MLN4924 for 24 h or 72 h. Metabolic activity was then measured by MTS assay. Cells treated with Triton X-100 (TX-100) served as a control for dead cells. Error bars show standard deviations.