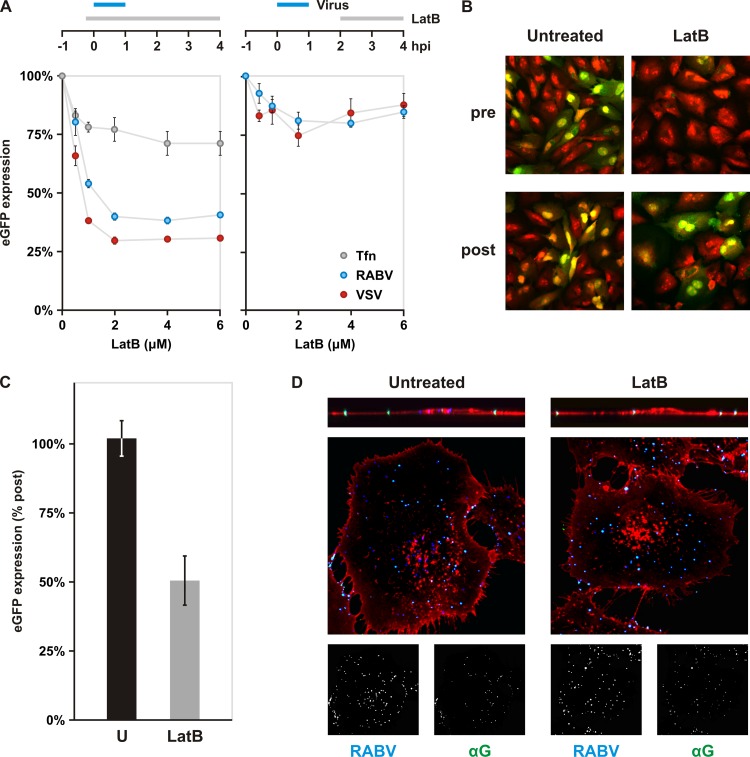
Fig 7.
Impact of actin depolymerization on rVSV RABV G internalization. (A) Impact of chemical depolymerization of actin on rVSV RABV G (RABV) and rVSV eGFP (VSV) infections. BS-C-1 cells were treated with various concentrations of latrunculin B (LatB) to inhibit polymerization of actin. As shown in the schematic, drug was added either 10 min prior to a 1-h inoculation with virus or at 2 hpi and maintained until analysis. eGFP expression was assayed by cytofluorimetry at 4 hpi. rVSV eGFP is shown in red and rVSV RABV G in blue. Uptake of fluorescent transferrin (Tfn, gray) is included as a control for general disruption of clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Cells were pretreated with LatB 10 min prior to Tfn addition. Cells were incubated with Tfn for 7 min. Following a wash with acid buffer to remove surface-bound Tfn, intracellular Tfn levels were measured by flow cytometry. (B) Effect of actin depolymerization on rRABV ΔG infection. BS-C-1 cells were treated with 6 μM LatB prior to inoculation (pre) or at 2 hpi (post). Expression of eGFP (green) from viral genomes was detected by confocal microscopy at 25 hpi. Cells were stained with propidium iodide (red). (C) Quantification of LatB effect on rRABV ΔG infection. BS-C-1 cells treated as for panel B were collected and analyzed for eGFP expression by flow cytometry. (D) Confocal microscopy of internalization assay in cells. Above the merged images are single-plane z-stack cross sections. Cells pretreated as indicated were inoculated with AF647-labeled rVSV RABV G (RABV), fixed, and stained with antibody against RABV G in the absence of permeabilization. The LatB concentration used was 1 μM. RABV (blue) and αG (green) signals are shown separately in inlays below the merged images. WGA is shown in red. Singly labeled, internalized particles appear blue; dually labeled, surface-bound particles appear cyan.