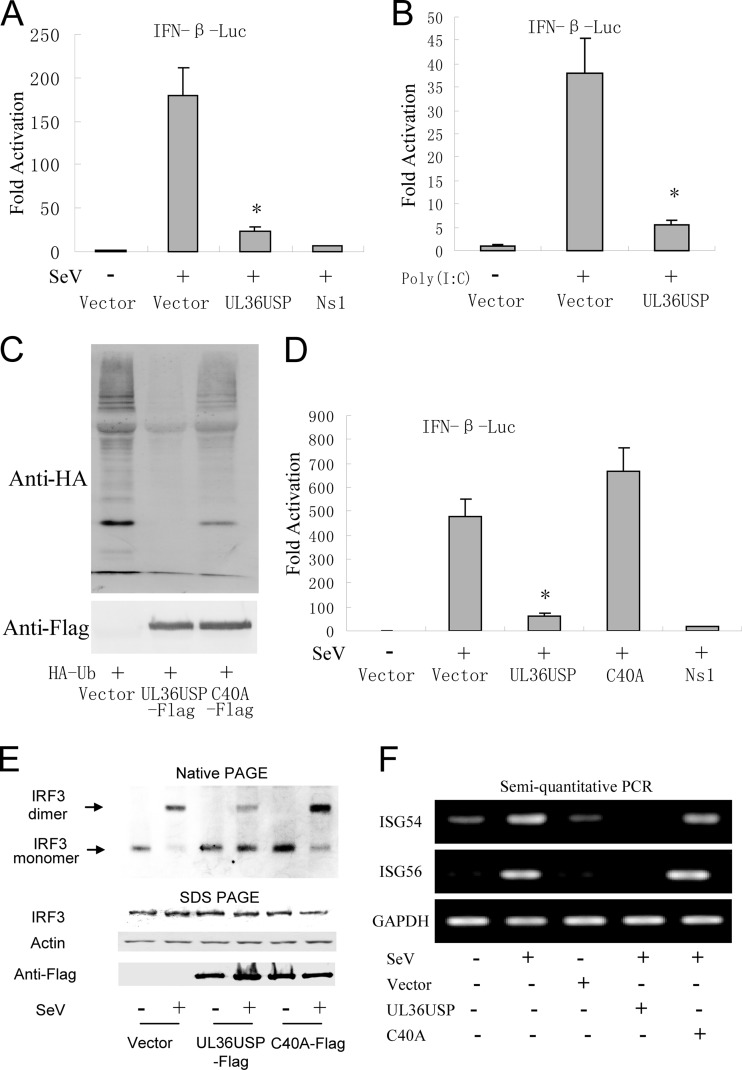
Fig 1.
HSV-1 UL36USP inhibits SeV-mediated IFN-β induction. UL36USP inhibits activation of IFN-β promoter, dimerization of IRF3, and transcription of ISGs. (A) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with IFN-β-Luc reporter plasmid, the pRL-TK control plasmid along with empty vector, and plasmids encoding UL36USP or influenza virus NS1 protein. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were infected with 100 HAU/ml SeV or mock infected, luciferase activity was measured 16 h postinfection, and fold activation was determined compared to that of the empty vector with mock infection. (B) UL36USP inhibited poly(I · C)-induced IFN-β promoter activity. IFN-β-Luc, pRL-TK, TLR3, UL36USP, and empty vector were transfected as indicated. After 24 h, 100 ng/ml poly(I · C) was transfected as indicated. Luciferase activity was measured as in panel A. (C) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with HA-Ub and control vector, UL36USP, or UL36USP with the C40A mutant. Western blotting was performed to examine the ubiquitination of total cell lysates. (D) DLR assays showed that the C40A mutant did not inhibit the SeV-mediated activation of the IFN-β promoter activity. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with the UL36USP and C40A expression plasmid. Twenty-four hours posttransfection, cells were mock infected or infected with SeV for 16 h. Whole-cell extracts were subjected to native PAGE and probed with anti-IRF3 antibody to detect IRF3 dimerization. (F) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis was then performed to detect the mRNA levels of ISG54 and ISG56.