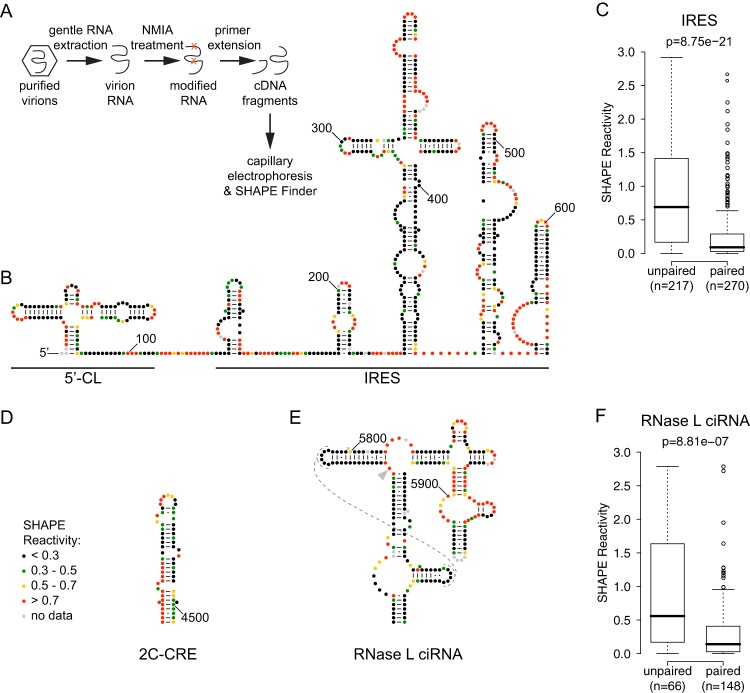
Fig 1.
Experimental procedure and SHAPE reactivities of previously described RNA structures in the poliovirus genome. (A) Outline of SHAPE experimental approach. (B) 5′ UTR: 5′-cloverleaf (5′-CL) and internal ribosome entry site (IRES). Accepted RNA secondary structure model for nt 1 to 625 of the poliovirus 1 (Mahoney) genome colored by SHAPE reactivity (constrained nucleotides are black, moderately reactive nucleotides are green or yellow, and flexible nucleotides are red). A-U and C-G base pairing is indicated by lines, and G-U (wobble) base pairing is indicated by dots. (C) Agreement of SHAPE with accepted structure for IRES. Box plots indicate median SHAPE reactivity, 25% and 75% quartiles, and 1.5× interquartile range for nucleotides predicted to be paired or unpaired; outliers are shown as open circles. (D) 2C-CRE. Nucleotides 4444 to 4504 are colored by SHAPE reactivity. (E) RNase L ciRNA. Nucleotides 5742 to 5968 are colored by SHAPE reactivity; dashed lines indicate predicted tertiary interaction; arrowhead indicates nucleotide 5775, site of the 3D-7000 A-to-U suppressor mutation that encodes the 3Cpro Y113F change. (F) Agreement of SHAPE with accepted structure for RNase L ciRNA. Box plots are as for panel A.