Fig 10.
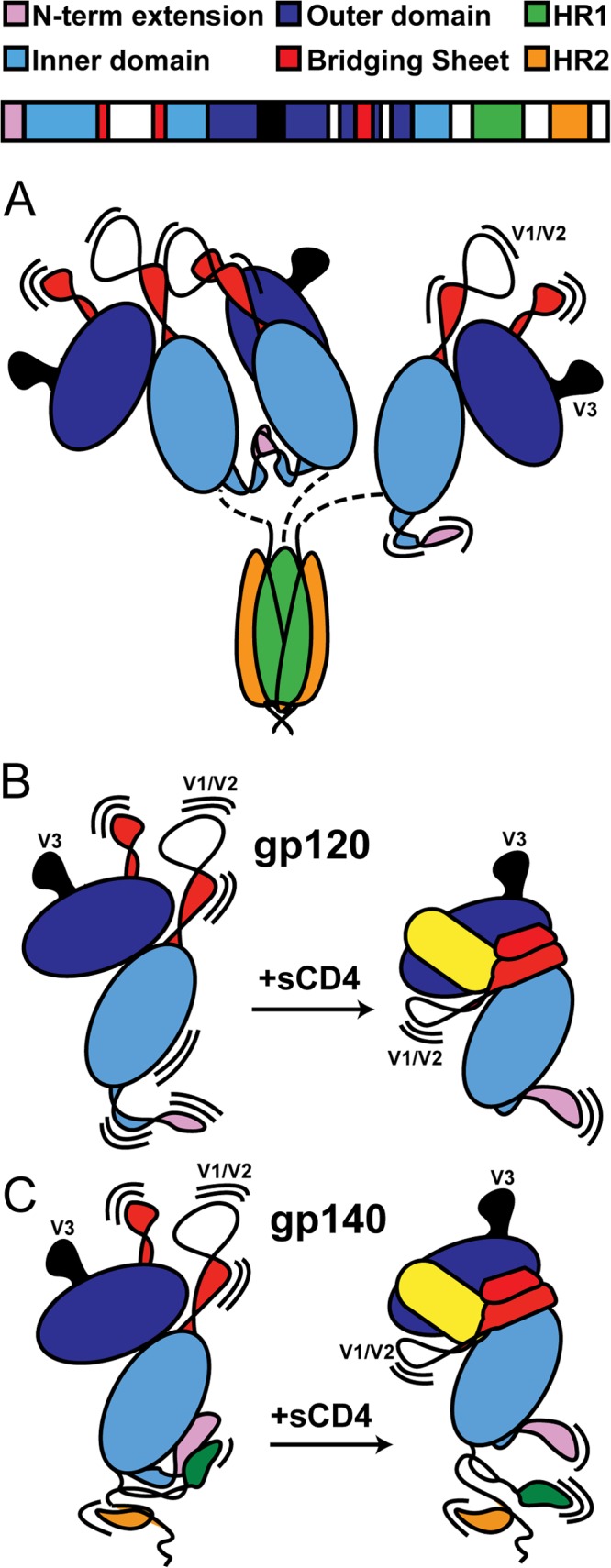
Structural models of various Env constructs. (A) gp140 trimers (and dimers) show no evidence of gp41/gp120 interactions. Instead, gp41 adopts a post-fusion-like state, while a portion of gp120s form dimers, presumably through contacts in V1/V2 and the N-terminal extension. (B) With monomeric gp120, CD4 (shown in yellow) binding stabilizes the gp120 inner domain, along with the elements that form the bridging sheet. (C) With monomeric gp140, CD4 has a similar effect on the bridging sheet but at the same time weakens the interface between gp120 and gp41, which involves the N- and C-terminal extensions of gp120 and HR1 of gp41. A color-coded sequence of gp140 is shown at the top, and the structural regions of interest are annotated in Fig. S1 to S3 in the supplemental material.
