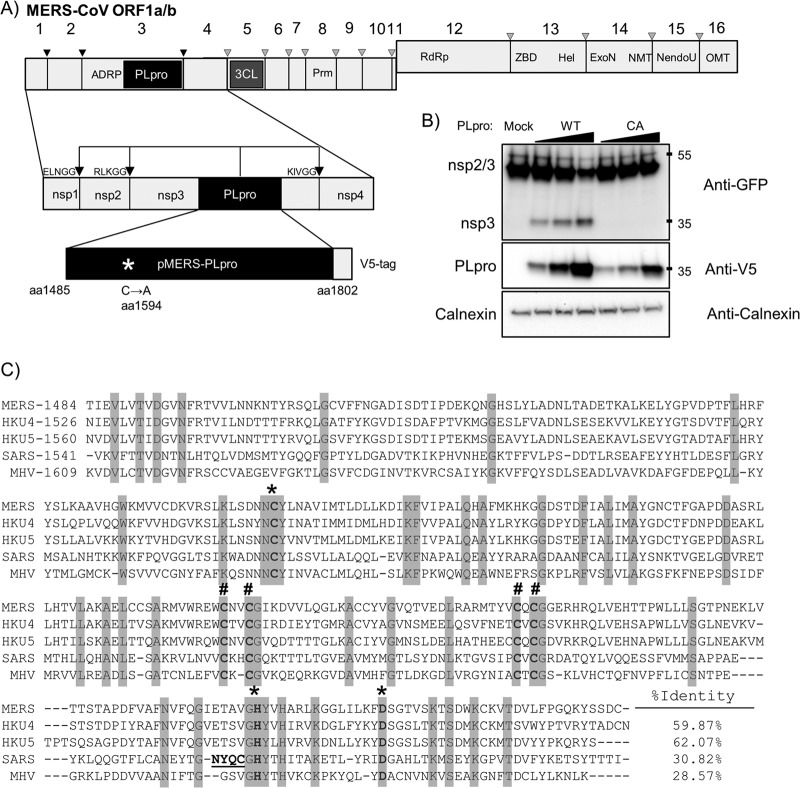
Fig 1.
Activity of MERS-CoV PLpro. (A) Schematic diagram of MERS-CoV ORF1a/b, with predicted PLpro cleavage sites indicated; pMERS-PLpro corresponds to amino acid residues (aa) 1485 to 1802. ADRP, ADP-ribose-1″-monophosphatase; PLpro, papain-like protease; 3CL, 3-chymotrypsin-like protease; Prm, primase; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; ZBD, zinc-binding domain; Hel, helicase; ExoN, exoribonuclease; NMT, N7 methyltransferase; NendoU, endoribonuclease; OMT, 2′ O-methyltransferase. (B) trans-cleavage activity of MERS-PLpro. pMERS-PLpro and plasmid DNA expressing the SARS-CoV nsp2/3-GFP substrate were transfected into HEK293T cells, lysates were harvested at 24 h posttransfection, and protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. WT, wild type. Numbers at the right are molecular masses (in kilodaltons). (C) Alignment of the PLpro domains from selected betacoronaviruses using the ViPR software MUSCLE alignment algorithm; identical residues are highlighted. *, catalytic residues; #, zinc-binding cysteines. Underlined residues in the SARS PLpro indicate a flexible loop that binds specific inhibitors. Accession numbers are as follows: for MERS-CoV amino acids 1484 to 1802, JX869059; for bat CoV-HKU4 amino acids 1526 to 1844, NC_009019; for bat CoV-HKU5 amino acids 1560 to 1878, NC_009020; for SARS-CoV amino acids 1541 to 1855, AY278741; and for MHV amino acids 1609 to 1911, NC_001846.