Fig 2.
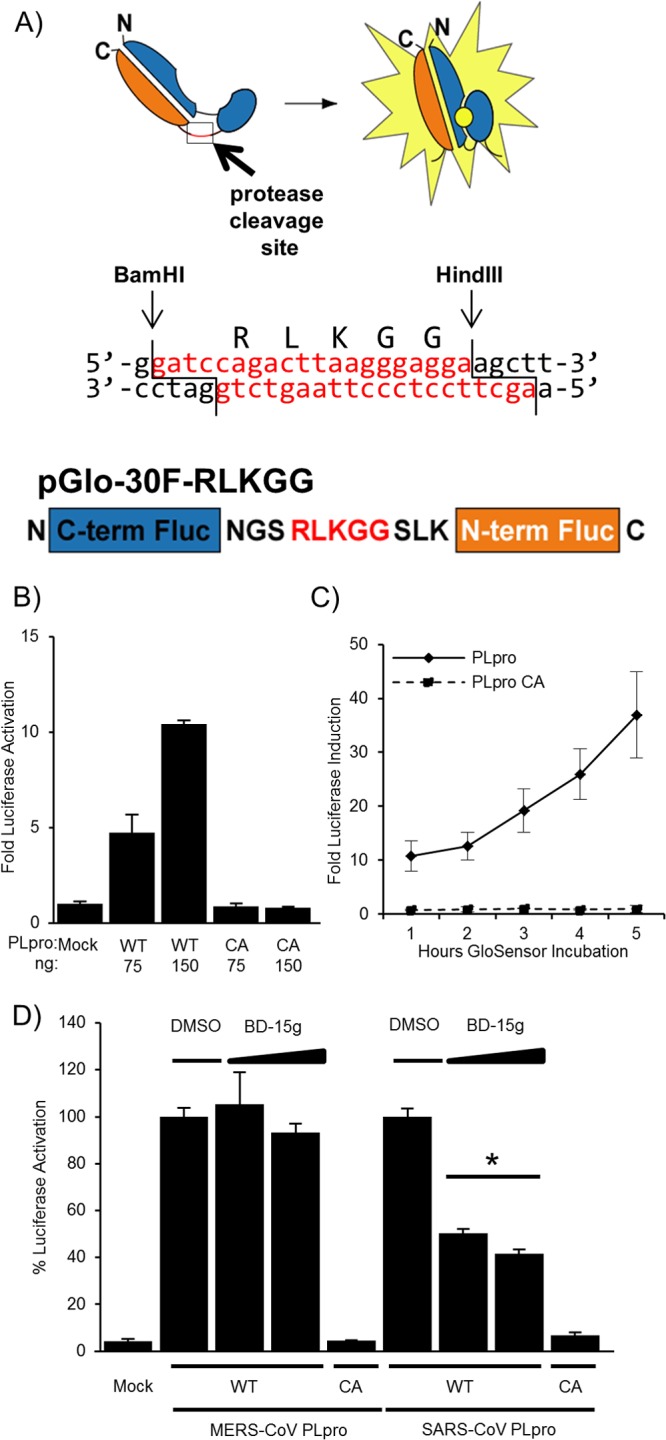
Biosensor assay detecting MERS-CoV PLpro activity in cells. (A) Diagram depicting the circularly permuted luciferase construct linked by the protease cleavage site RLKGG for assessing CoV PLpro activity. (B) Expression of MERS-CoV PLpro activates the biosensor. HEK293T cells are cotransfected with pGlo-30F-RLKGG and either pMERS-PLpro or pMERS-PLpro-CA. At 20 h posttransfection, cells were lysed and assayed using the dual-luciferase assay. The experiment was performed in triplicate, and error bars represent the standard deviations of the means. (C) Live-cell assay of MERS-PLpro activity. Cells were cotransfected with pGlo-30F-RLKGG and either pMERS-PLpro or pMERS-PLpro-CA. At 14 h posttransfection, cells were incubated with GloSensor reagent, and luminescence was read hourly. The experiment was performed in triplicate, and error bars represent the standard deviations of the means. (D) A previously identified SARS-CoV inhibitor does not inhibit MERS-CoV PLpro. HEK293T cells were transfected with the wild-type (WT) or catalytic-mutant (CA) SARS-CoV PLpro or MERS-CoV PLpro and pGlo-RLKGG constructs for 13 h and then treated with 12.5 or 6.25 μM BD-15g for 3 h or with the equivalent volume of DMSO diluted in medium. Cells were then lysed and assayed for dual-luciferase activity. The experiment was performed in triplicate, with error bars representing the standard deviations of the averages. *, P < 0.005, as determined with Student's t test between DMSO- and drug-treated cells.
