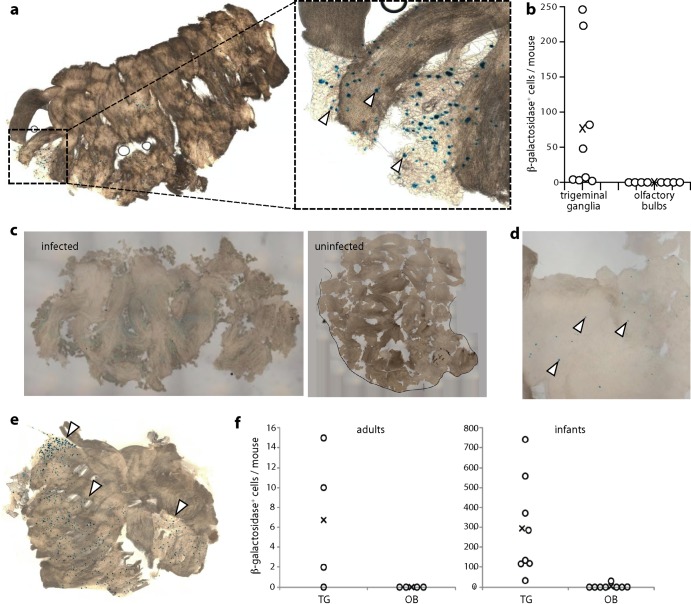
Fig 4.
Floxed reporter gene activation by viral Cre recombinase. (a) ROSA26R mice (6 to 8 weeks old), which have a floxed β-galactosidase expression cassette activated by Cre recombinase, were infected i.n. (106 PFU) with HSV-1 expressing Cre from an HCMV IE1 promoter (HSV-Cre). Ten days later, TG and OB were removed, fixed, incubated with X-Gal, and examined for β-galactosidase-positive cells (blue spots). A representative infected TG is shown. The arrows in the zoomed image show example positive cells. Uninfected ROSA26R mice and infected, nontransgenic C57BL/6 controls showed no blue spots. (b) Mice were infected and analyzed as described for panel a, and blue spots were counted for TG and OB. Circles show individual mice, and exes show means. All TG contained blue cells, although the number per mouse was variable. No OB contained blue cells. (c) An OB of a strongly infected ROSA26R mouse inoculated i.n. 10 days earlier with HSV-Cre and developed with X-Gal showed a faint blue wash, but no blue cells. The blue wash possibly reflected enzyme or converted substrate leaking from the axons of β-galactosidase-positive primary olfactory neurons. An uninfected OB is shown for comparison. (d) At 20 days after i.n. HSV-Cre inoculation of a 1-week-old mouse, an OB shows a few, scattered blue cells (arrows). Magnification is ×5 relative to that of panel c. (e) A TG from the same mouse shows large numbers of blue-staining cells (arrows). (f) Eight-week-old (adult) or 1-week-old (infant) ROSA26R mice were infected with HSV-Cre and 20 days later analyzed for β-galactosidase expression in TG and OB. Circles show individual mice, and exes show means. Three out of four adult and 8/8 infant TG and 0/4 adult and 1/8 infant OB contained blue cells. In this experiment, adult TG blue cell counts were at the lower end of the range seen in panel b, and infant counts were 50-fold higher.