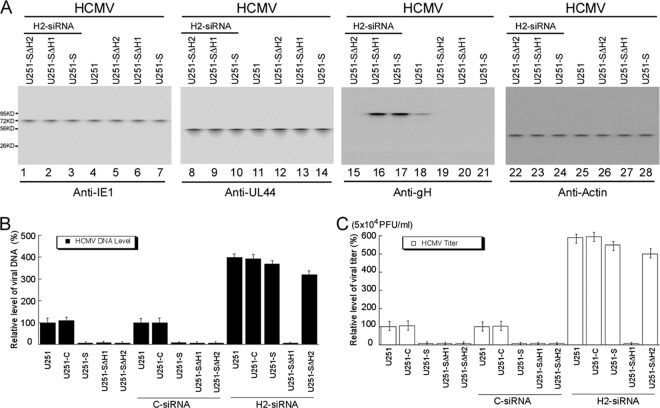
Fig 9.
Effect of altered expression of Snapin on HCMV gene expression and viral genomic synthesis and production. (A) Western blot analysis was used to assay the levels of HCMV IE1, UL44, and gH in the parental U251 cells (U251; lanes 4, 11, 18, and 25), cells overexpressing full-length Snapin (U251-S; lanes 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, 21, 24, and 28), and Snapin mutants SΔH1(37-65aa) (U251-ΔH1; lanes 2, 6, 9, 13, 16, 20, 23, and 27) and SΔH2(81-126aa) (U251-SΔH2; lanes 1, 5, 8, 12, 15, 19, 22, and 26). Cells were either transfected with anti-Snapin H2-siRNA (H2-siRNA; lanes 1 to 3, 8 to 10, 15 to 17, and 22 to 24) or not transfected with any siRNAs (lanes 4 to 7, 11 to 14, 18 to 21, and 25 to 28), infected with HCMV at an MOI of 1 at 48 h posttransfection, and harvested at 48 to 72 h postinfection. The expression of cellular actin was used as the internal loading control. (B) To assay the level of intracellular viral DNA, cells were harvested at 72 h postinfection. (C) Total infection cultures were collected at 5 days postinfection, and viral titers were determined. The values of the relative HCMV titers and levels of DNA, which are the means from three independent experiments, represent the ratios of the viral titers or levels of DNA in different cells to those in the parental U251 cells (U251), respectively. The viral titers in parental U251 cells were 5 × 104 PFU/ml. The analyses were repeated three times, and the standard deviations are indicated by the error bars.