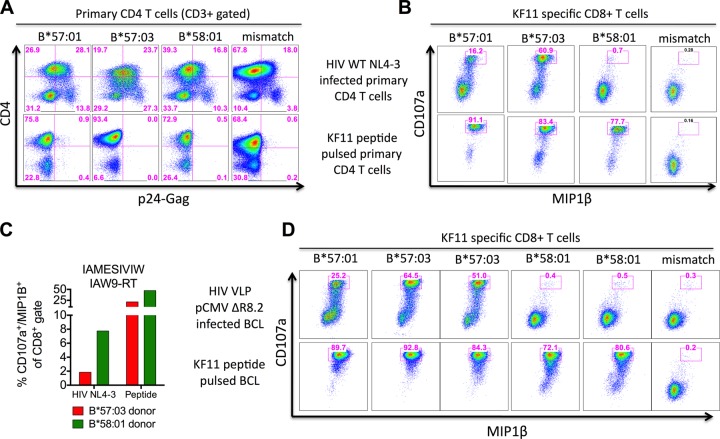
Fig 3.
Lack of intracellular KF11 epitope processing within HLA-B*58:01-expressing target cells. (A) Primary CD4 T cells derived from healthy uninfected individuals expressing the indicated HLA-B molecule (B*57:01, donor A; B*57:03, donor B; B*58:01, donor C; HLA mismatch, donor D) (data not shown) were activated for 7 days and synchronously infected with wild-type HIVNL4-3 (data not shown). (B) After 48 h of infection, the cells were cocultured with the KF11-specific CD8+ T-cell line for 6 h in the presence of brefeldin A, stained for CD107a/MIP1β expression to measure KF11 epitope presentation on the surfaces of infected cells, and controlled by KF11 peptide pulsing of uninfected target cells at 3 nM. Representative results from one of two experiments are shown. (C) As described for panel B but using CD8+ T cells recognizing the Pol-RT epitope IAMESIVIW (AW9-RT) after HIVNL4-3 infection and shown with HLA mismatch background subtraction (8%). (D) B cell lines derived from 6 individuals expressing the relevant HLA-B molecule shown above each dot plot were infected with the HIV virus-like particle (HIV VLP pCMVΔR8.2) (data not shown) for 24 h, cocultured with the KF11-specific CD8+ T-cell line for 6 h, and controlled by KF11 peptide pulsing of uninfected B cell lines as described for panel B. Results from one of two independent experiments are shown.