Fig 6.
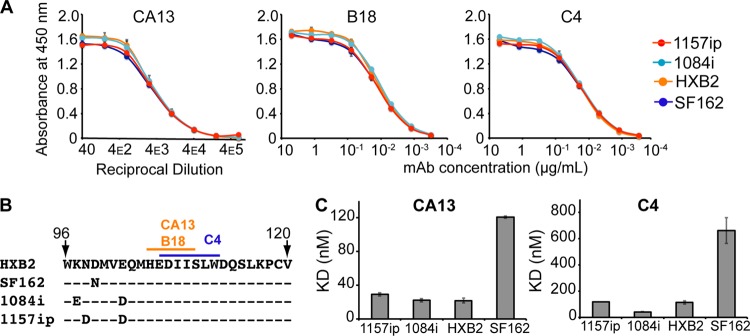
Linear epitope-specific antibody binding to a region of gp120 differentially stabilized across isolates. (A) Linear epitope-specific antibody (CA13, B18, or C4) binding to gp120 proteins measured by the ELISA. The curves are color coded by Env isolate as defined in the symbol key. Concentrations of monoclonal antibodies (mAb) are shown on the x axis for C4 and B18, and the reciprocal dilution of antibody supernatant is shown on the x axis for CA13. Curves are representative of at least two independent experiments; error bars indicate standard deviations from duplicate measurements. (B) The primary sequence recognized by antibodies CA13, B18, and C4 is absolutely conserved among the four gp120s. A dash indicates that the residue is conserved in a given isolate, and amino acid differences are indicated. This region is differentially stabilized in the four gp120s, based on HDX-MS (Fig. 3B) (C) Summary of SPR-derived binding constants for CA13 and C4 binding to the four gp120s. Raw and fitted SPR curves are shown in Fig. S20 in the supplemental material. The B18-gp120 SPR binding curves did not fit well to a 1:1 binding model; therefore, estimates of affinity are not available, although qualitative isolate-specific differences in binding to B18 were similar to those observed for CA13 and C4 (see Fig. S20). Error bars indicate standard deviations, calculated as described in Materials and Methods.
