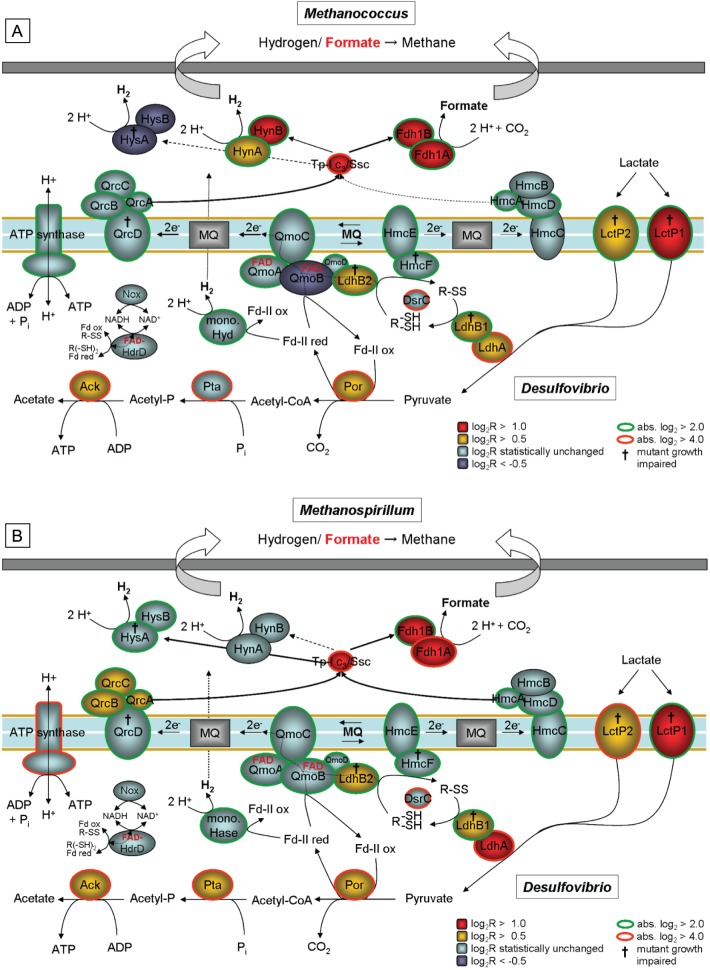
Fig 8.
Proposed metabolic models for syntrophic growth of D. alaskensis G20 at the low growth rate of 0.027 h−1 with either M. maripaludis (A) or M. hungatei (B). Colors indicate transcriptional changes in individual genes during coculture growth relative to a sulfate-limited monoculture (the main electron transfer pathway in respective Desulfovibrio species is highlighted with red arrows); D. alaskensis G20 mutants with no growth in coculture on lactate are marked with the symbol “†” (the coculture mutant phenotypes with M. maripaludis were determined in an earlier study [15]). Abbreviations used: LctP, lactate permease; Ldh, lactate dehydrogenase; R-(SH)2 and R-SS, reduced and oxidized form of unknown thiol/disulfide redox pair (probably DsrC) interacting as electron carrier with Ldh; Por, pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; Fdred and Fdox, reduced and oxidized form of ferredoxin; Qmo, quinone-interacting membrane-bound oxidoreductase; MQ, menaquinone; Qrc, quinone reduction complex; Pta, phosphate acetyltransferase; Ack, acetate kinease; Aor, aldehyde:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; Adh, alcohol dehydrogenase; Hdr-Flox, putative electron-bifurcating complex coupling NADH oxidation with reduction of thiol/disulfide redox pair (probably DsrC) and ferredoxin and vice versa (electron confurcation); Hmc, high-molecular-weight cytochrome c complex; Hyn, [NiFe] hydrogenase; Fdh, formate dehydrogenase; Hyd, [Fe] hydrogenase; TpIc3, type I cytochrome c3; Ssc, split-soret cytochrome c; CoA, coenzyme A.