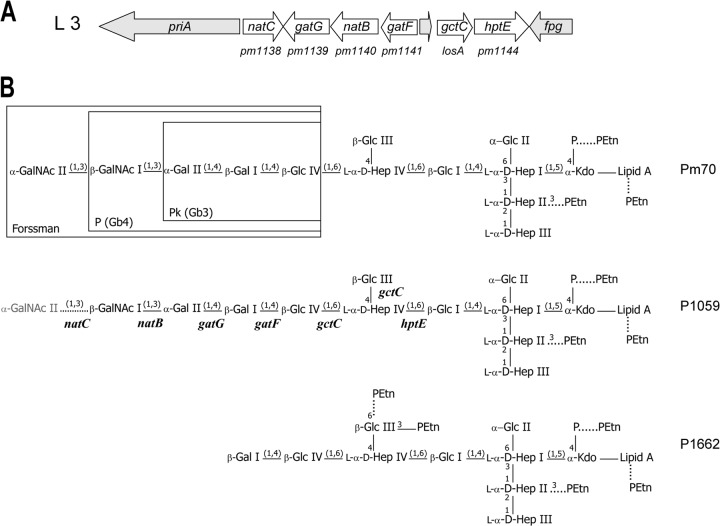
Fig 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the genetic organization of the P. multocida L3 LPS outer core biosynthesis locus, which is common to serovars 3 and 4. Genes involved in LPS outer core assembly are shown in white. Conserved genes unrelated to LPS biosynthesis are shown in gray. Original gene annotation numbers for Pm70 are shown below the diagram. (B) Schematic representation of the LPS structure expressed by the P. multocida serovar 3 and 4 type strains (P1059 and P1662, respectively). Only inner core glycoform A is shown. The P. multocida glycosyltransferase genes predicted to be required for assembly of the outer core are shown below each linkage on the structure expressed by P1059. The rare addition of GalNAc II onto the P1059 LPS is shown with a dotted line and in gray. The specific number and position of phosphoethanolamine (PEtn) residues attached to each LPS structure are strain dependent; nonstoichiometric additions of PEtn are shown with dotted lines. Regions of the L3 LPS that are identical to the oligosaccharide components of the vertebrate glycosphingolipids, Forssman, P, and Pk, are shown boxed in the Pm70 structure. GalNAc, N-acetyl-galactosamine; Gal, galactose; Glc, glucose; Hep, heptose; PEtn, phosphoethanolamine; Kdo, 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid; P, phosphate.