Figure 1.
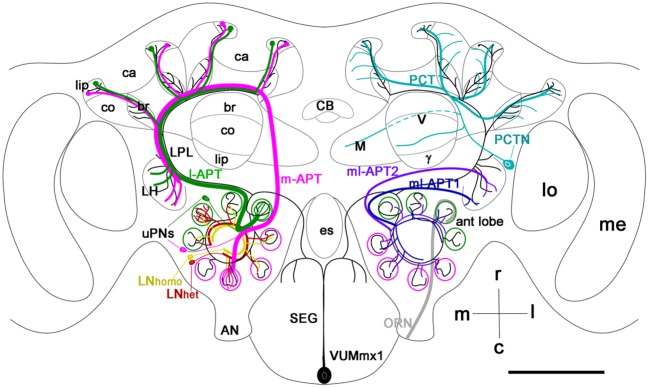
Schematic view of the main olfactory pathways in the honey bee brain (based on Fonta et al., 1993; Abel et al., 2001; Strausfeld, 2002; Sinakevitch et al., 2005, 2011; Kelber et al., 2006; Kirschner et al., 2006; Schröter et al., 2007; Girardin et al., 2013). Olfactory Receptor Neuron (ORN) axons from the antenna enter through the antennal nerve (AN) into the antennal lobe (ant lobe) and converge onto the outer cortex of glomeruli. Each glomerulus is innervated by processes of several types of neurons. Uniglomerular projection neurons (uPNs magenta and green) have dendritic branches in a single glomerulus and send axons to higher-order brain centers such as the MB calyces (ca), lateral protocerbral lobe (LPL), and lateral horn (LH). There are two uniglomerular antenno-protocerebral tracts, the l-APT (green) and m-APT (magenta), which reflect the segregation of glomeruli into rostral (l-APT) and caudal (m-APT) hemispherical clusters. Kenyon cells (not shown in the figure) are the intrinsic cells that make up the MB. Kenyon cell dendrites form pairs of calyces (ca) with specific zones that receive different types of inputs, the lip, collar (co), and basal ring (br). The lip and br are innervated by uPN axons. The Kenyon cell axons project ventrally and split to form medal (M), vertical (V), and γ lobes, which are the main output regions of the MB. Protocerebral tract neurons (PCTN) receive inputs in the lobes and provide GABAergic feedback to the calyces. Multiglomerular PNs project axons via the medio-lateral protocerebral tracts (ml-APT 1,2) to the LPL and LH. At least two types of local interneurons (LN) interconnect glomeruli within the AL, homogeneous LNhomo (yellow), and heterogeneous LNhet (red). Ventral unpaired median neurons (VUM) have cell bodies in the maxillary (VUMmx1 is shown) and mandibullar neuromeres of the subesophageal (SEG) ganglion and connect gustatory processing in the SEG to all antennal lobe glomeruli, the LPL, LH, and MB calyces. CB, central body; M, medial lobe; V, vertical lobe; γ, gamma lobe; lo, lobula; me, medulla; m, median; l, lateral; r, rostral; c, caudal. Cell types in each side of the brain are bilaterally symmetric, but for clarity different cells are shown in each half. Scale bar: 250 μm.
