Figure 2.
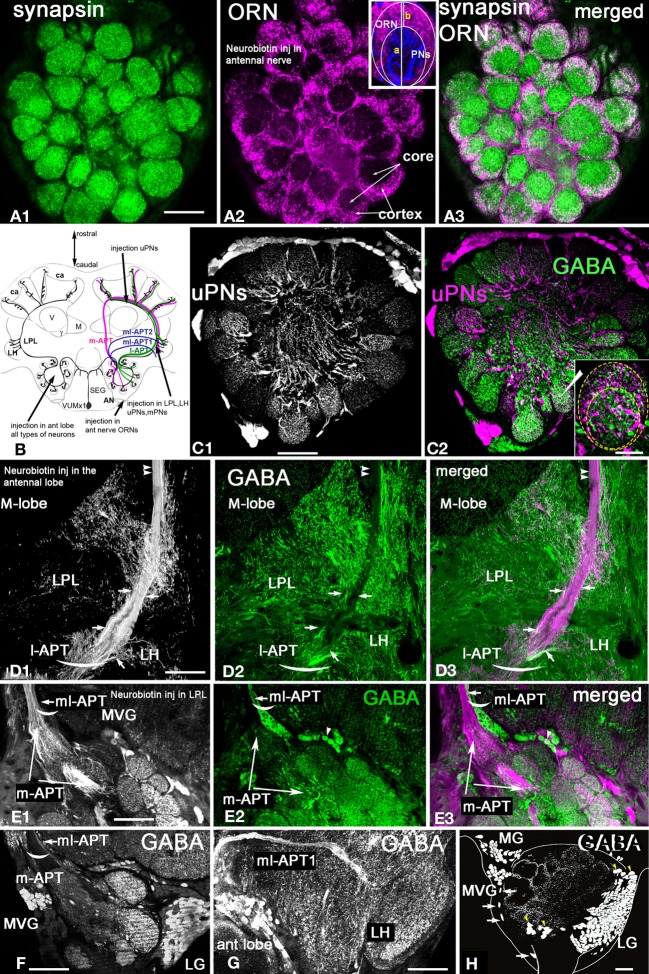
Apis mellifera. General morphology of the antennal lobe and glomerulus. GABAergic neurons in the honeybee antennal lobe are local interneurons and multiglomerular PNs that branch into LPL and LP. (A) Frontal section of the honeybee antennal lobe immunostained with anti-synapsin antibodies (green) and Rhodamine-dextran labeled olfactory receptors neurons (magenta). (A1) Anti-synapsin (green) shapes the synaptic neuropil of the antennal lobe in all glomeruli, highlighting the potential synaptic connections between different types of neurons. (A2) Rhodamine-dextran injection into the antennal nerve revealed olfactory receptor neuron (ORN) endings (magenta) surrounding each glomerulus to form the cortex layer. The core area of glomerulus is free of ORNs. (A3) The merged images of the cortex area of the ORN endings in the antennal lobe overlapped with the area marked by anti-synapsin (white) indicate that ORNs synapse and receive synapses from other antennal lobe neurons in the cortex rind of glomerulus. Insert in (A2): The schematic of the glomerulus overlaid on the middle section indicated by the image of the projection neuron dendrite (blue, PNs) and ORNs (magenta). The distribution of PN dendrites in the core and cortex of the glomerulus in the section made through the midline of the glomerulus demonstrates that large axons of PNs are in the core area and fine dendrites of PNs in the cortex where they overlap with ORNs: b-the length of the cortex area in the center, a-the length of the glomerulus. (B) Schematic view of the olfactory pathways in the brain of the honey bee where arrows show the site of Rhodamine-dextran or/and neurobiotin injections. The octopaminergic neuron VUMmx1 has a cell body in the subesophageal ganglion (SEG) and carries information along the olfactory pathway from the antennal lobe to the lateral horn (LH), lateral protocerebral lobe (LPL), and the MB calyx (ca). The tracts that carry the uniglomerular PNs are l-APT and m-APT, while the two tracts for multiglomerular mPNs are ml-APT 1,2. (C) Double stainings of uPNs (magenta) and anti-GABA (green) in the antennal lobe demonstrate that uniglomerular PNs are not GABAergic. (C1) Injection into the l-APT and m-APT as indicated in (B) revealed uPNs with dendrites in both core and cortex areas of glomeruli. (C2) Merged images of GABA (green) and uPNs (magenta) indicate that cell bodies of the uPNs are not GABAergic. White labeling in the glomerulus is due to overloaded dye in PNs and not co-localization, as illustrated in the image of the glomerulus with uPN dendrites and anti-GABA staining in the insert of (C2). (D) Double labeling of the l-APT (D1 single image) and anti-GABA (D2 green single image) on the frontal section of the honey bee protocerebrum. The l-APT stained by injection in the antennal lobe (D3) The merged image illustrates that the two axons framing l-APT are GABAergic (white) and connect to the lateral protocerebrum (LH), another l-APT GABAergic fiber originating from antennal lobe branches in the lateral protocerbral lobe (LPL). Double arrows indicate the absence of anti-GABA in the uPN l-APT axons before their entry to the MB calyx. (E) Double staining of the m-APT and ml-APT revealed by injection of dye into LPL (single image E1, magenta in E3) and anti-GABA (green in E1and E2) (E1) uPNs in m-APT tract (E2) Anti-GABA staining manifests only in the section that we identify as the beginning of the ml-APT (E3) The m-APT is not stained with GABA, however a few GABAergic fibers are in the m-APT. These fibers are in the lateral part of the m-APT exiting from the antennal lobe that we identified as ml-APT 1,2(white merge image). (F) GABA staining in the m-APT and the two groups of GABAergic neurons in the frontal section of the antennal lobe are made in the area of the m-APT tract. The axons from the ml-APT are indicated by arrows. (G) GABA staining is in the ml-APT-1 that branches to the ventral part of the LH. (H) Schematic presentation of GABAergic cell clusters made after ten frontal brain sections (35 μm each) stained with GABA. The three groups of neurons identified are MVG, MG, and LG. Four neurons are identified as Giant MVG GABAergic neurons: they have a defined location and large somata (arrows). All figures show the right part of the brain: the middle of the brain is on the left and the lateral on the right. V, vertical lobe; γ, gamma lobe of MB. Scale bar: A, C–H = 35 μm; insert in C2 = 15 μm.