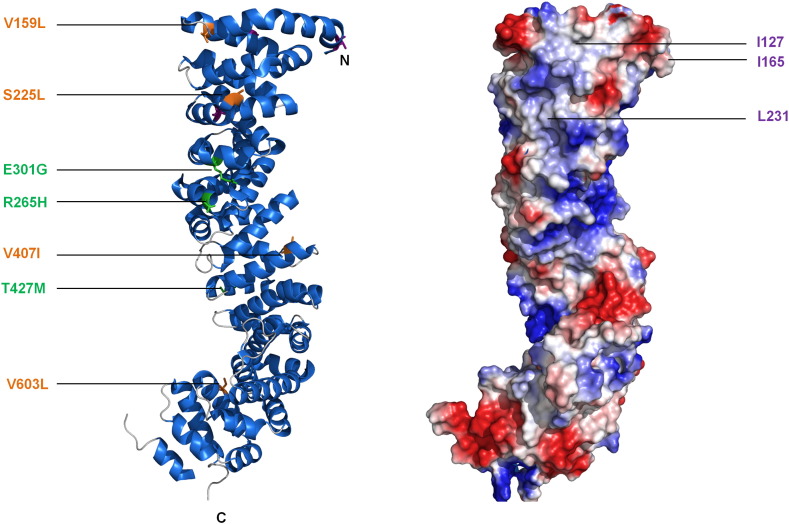
Fig. 3.
Plakoglobin structure and locations of ARVC mutations. Crystal structure of the plakoglobin arm domain (PDB code: 3IFQ) (left) and electrostatic potential of surface-exposed residues (right). In the ribbon diagram, point mutations that are known to be pathogenic are shown as either copper (buried) or green (surface exposed). Although plakoglobin exhibits comparatively fewer pathogenic mutations than other desmosomal proteins, they are balanced between exposed and buried positions across the domain, with consequences on protein stability and binding properties that require further examination. In the electrostatic potential map, blue and red represent positively and negatively charged regions, respectively. The surface shows the charged E-cadherin binding groove, which is also proposed to bind to desmoglein and desmocollin [95]. Amino acids proposed to mediate desmoglein and desmocollin binding are highlighted in purple [95].