Figure 1. DhbE Catalyzed Aryl Acid Activation and the Yeast Selection Scheme to Change the Substrate Specificity of DhbE.
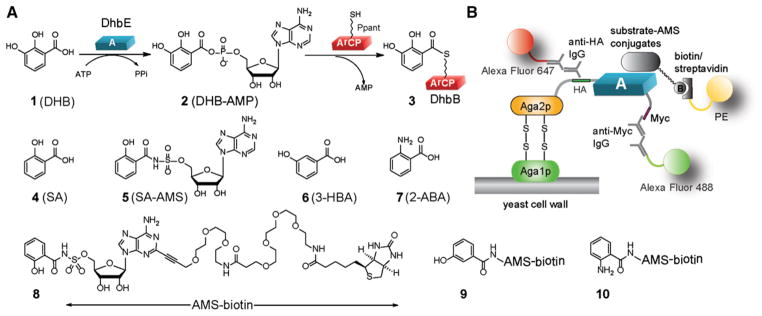
(A) DhbE catalyzes the condensation of DHB 1 with ATP to form DHB-AMP 2. The activated DHB is then transferred to the ArCP domain of DhbB to form a thioester conjugate 3 with the Ppant group of ArCP. DhbE can also activate SA 4. SA-AMS conjugate 5 is a bisubstrate inhibitor of DhbE. Structures of 3-HBA 6 and 2-ABA 7 as examples of nonnative substrates of DhbE are also shown.
(B) Selection of the A-domain library displayed on the surface of yeast cells. AMS-biotin conjugated SA (8) is used in the model selection to test the binding of wtDhbE on yeast cell surface with substrate-AMS conjugate. Compounds 9 and 10 have nonnative substrates 3-HBA 6 and 2-ABA 7 conjugated to AMS-biotin. They were used in the selection of DhbE mutants by yeast cell surface display.
See also Figures S1–S14 and Tables S1 and S3.
