Figure 2.
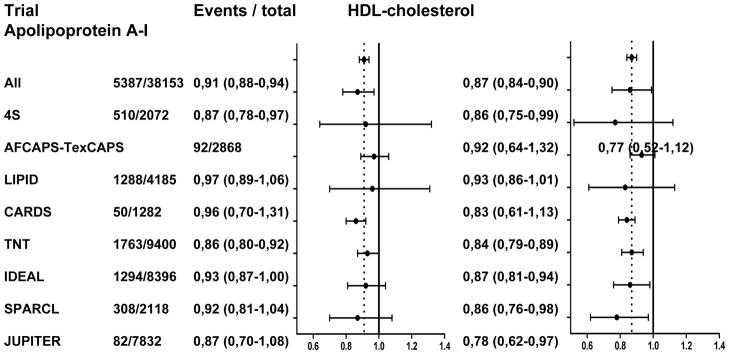
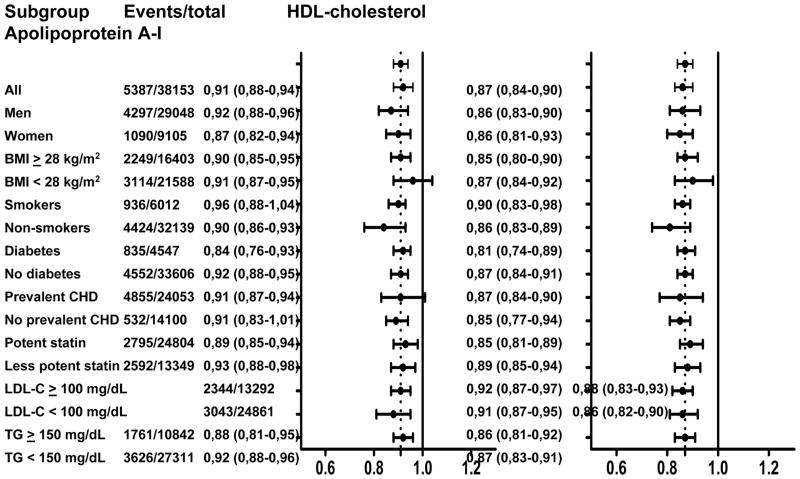
Figure 2A. Association between on-statin HDL cholesterol or apolipoprotein A-I and risk of major cardiovascular events by baseline characteristics
Figure 2B. Association between on-statin HDL cholesterol or apolipoprotein A-I and risk of major cardiovascular events stratified by trial
Data presented for each subgroup or trial are the number of major cardiovascular events / total number of study participants in that subgroup or trial, hazard ratio and corresponding 95% confidence interval for risk of major cardiovascular events per 1 standard deviation increase of HDL cholesterol, and equivalent hazard ratio for apolipoprotein A-I. Graphics represent hazard ratios (dots) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (horizontal lines). Vertical dotted line represents point estimate for all participants combined. Hazard ratios were adjusted for trial, sex, age, smoking status, diabetes mellitus, systolic blood pressure, body mass index, glucose, and non-HDL cholesterol. HDL = high-density lipoprotein, BMI = body mass index, LDL-C = low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, CHD = coronary heart disease, TG = triglycerides