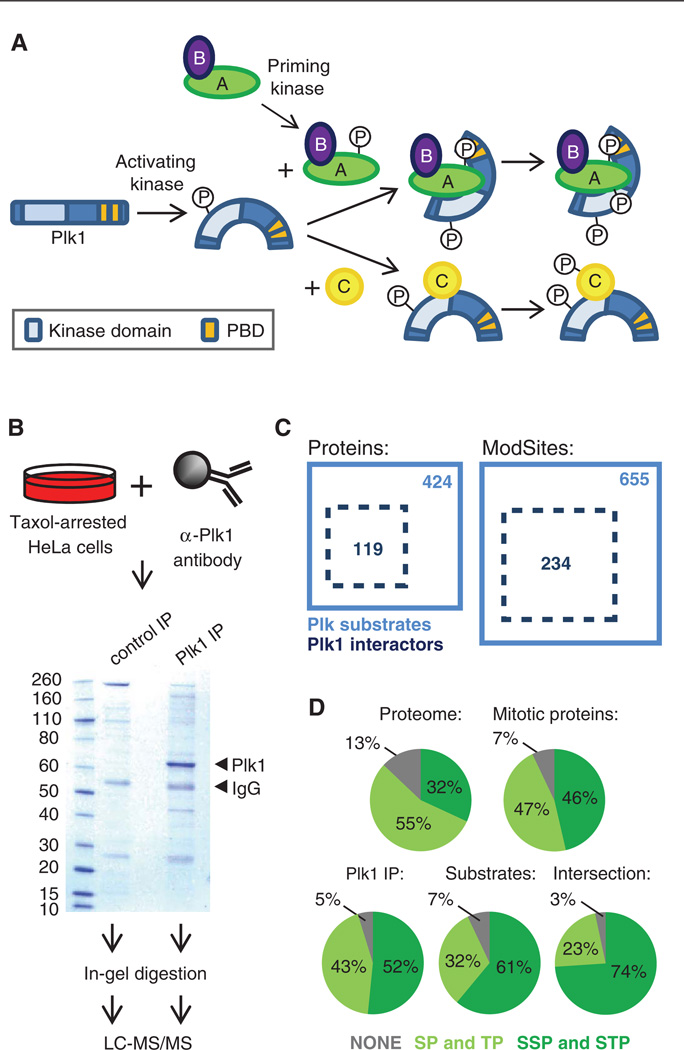
Fig. 7.
Identification of Plk1-interacting proteins. (A) Schematic of the mechanism of Plk1 activation and substrate recognition. Phosphorylation of Plk1 at Thr210 by kinases, such as Aurora A, leads to its activation. Through its Polo-box domain (PBD), Plk1 recognizes and interacts with some of its substrates, which have previously been phosphorylated by a priming kinase at an Sp[S/T]P sequence, leading to additional phosphorylation of these substrates by Plk1. PBD-independent interactions of Plk1 and substrates, which subsequently lead to phosphorylation of these substrates by Plk1, are also possible. (B) Scheme and Coomassie gel of Plk1 immunoprecipitation (IP). Plk1 and IgG bands are indicated by arrows. Substrates of Plk1 that interact directly with Plk1 through the PDB (labeled as A in panel A) or through other sites (labeled as C in panel A), as well as proteins bound to PBD-binding partners (secondary interactions, labeled as B in panel A) and direct Plk1-interacting proteins that are not substrates (not shown in panel A) are expected to coprecipitate. (C) Diagram of overlap of proteins and unique ModSites identified as Plk1 interactors by Plk1 IP (dotted black box) and Plk substrates identified in the large-scale phosphoproteomics experiments with BI2526 (solid blue box). (D) Distribution of [S/T]P and S[S/T]P sites in the whole proteome, in the 6061 proteins identified across all experiments (mitotic proteins), in all Plk1-interacting proteins identified in the Plk1 IP, in the 424 BI2536-sensitive candidate substrates, and in the 119 protein intersection of BI2536-sensitive substrates that were also in the Plk1 IP.