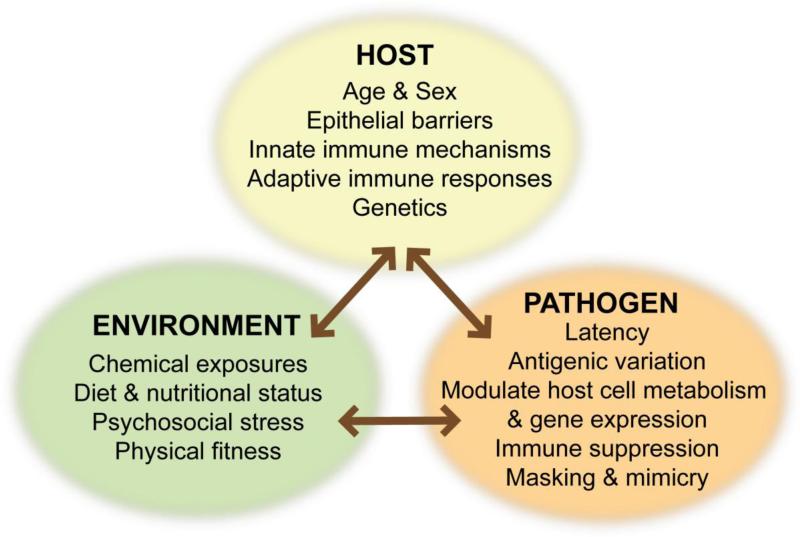
Figure 1. Host-Environment-Pathogen Interactions.
Differences in host genetics, age, and sex have long been known to influence outcomes following infection. Likewise, pathogen-specific mechanisms have evolved to evade host defenses, and continue to gain appreciation. Fewer studies have considered the impact of environmental differences on the host or the pathogen. Yet, when examined, emerging data provide compelling evidence that extrinsic factors, such as exposure to chemicals, psychosocial stress, and dietary constituents have a profound influence.