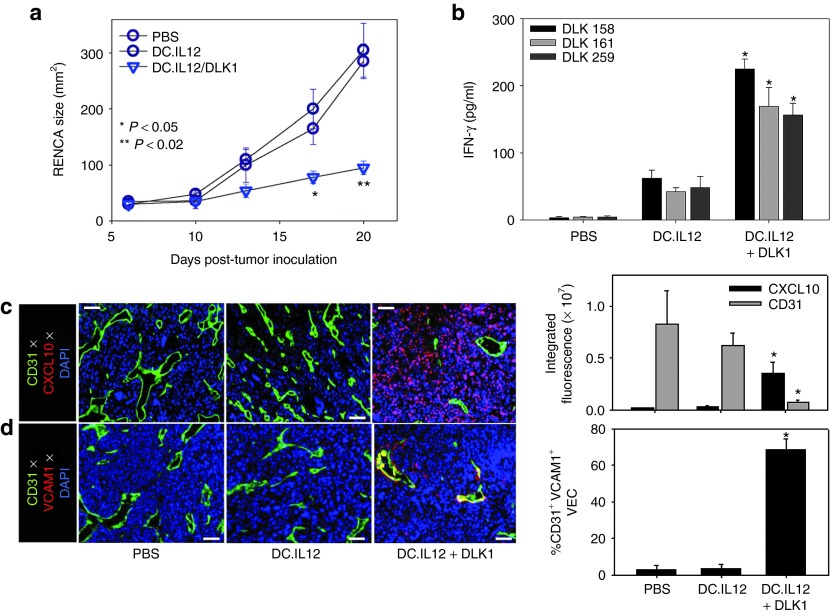
Figure 2.
DC/DLK1 peptide-based vaccines are both immunogenic and therapeutic in the murine RENCA model of RCC. BALB/c mice were inoculated with RENCA tumor cells s.c. on the right flank on day 0. (a) After randomizing for similar mean tumor size per treatment cohort (n = 5), mice were injected s.c. on their left flank on days 7 and 14 (post-tumor inoculation) with PBS, 106 DC.IL12 or 106 DC.IL12 pre-pulsed with equimolar mix (10 μmol/l each) of the three synthetic DLK1 peptides. Tumor growth (mean ± SD) was then monitored over time. (b) On day 21 post-tumor inoculation, splenic CD8+ T cells were isolated from each cohort and co-cultured with syngenic DC pre-pulsed with individual DLK1 peptides for 24 hours, at which time, IFN-γ ELISA were performed on the harvested cell-free supernatants. (c,d) Day 21 tumors were fixed, sectioned and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy; CD31 (green in c,d), CXCL10 (red in c), VCAM1 (red in d). The percentage of VCAM1 co-localization with CD31 is depicted as a yellow signal in d and was quantitated using Metamorph software as described in Materials and Methods. Histograms to the right of images reflect mean fluorescence intensity quantitation of the indicated markers (±SD) from three independent fields per slide as described in Materials and Methods. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed. *P < 0.05 versus control treatments (analysis of variance). DC, dendritic cell; IFN, interferon; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; RCC, renal cell carcinoma.