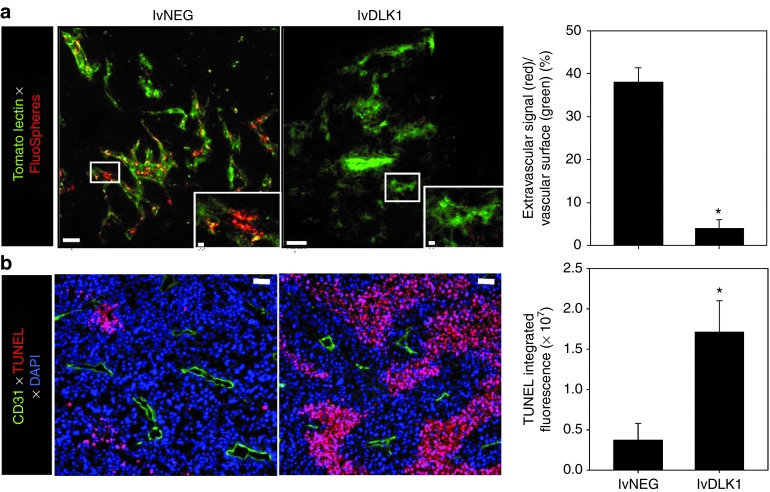
Figure 5.
Recombinant lvDLK1-based vaccination reduces tumor vascular permeability resulting in the development of apoptotic “dead zones” in the TME. In repeated experiments as outlined in Figure 3, (a) treated mice received intravenous injections of tomato lectin-FITC to label vascular endothelium (green) and 20 nm FluorSpheres to assess vascular permeability (red) on day 24 post-tumor inoculation. Whole tumor tissue was then imaged immediately by confocal microscopy at a depth of 17 μm. *P < 0.05 for lvDLK1 versus lvNEG (t-test). (b) On the same day, unlabeled mice were euthanized, with tumors resected, fixed, sectioned, and analyzed for expression of CD31 (green) and apoptotic nuclear staining with TUNEL reagent (red). Histograms to the right of images reflect mean fluorescence intensity quantitation of the indicated markers (±SD) from three independent fields per slide as described in Materials and Methods. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed. *P < 0.05 for lvDLK1 versus lvNEG (t-test).