Figure 5.
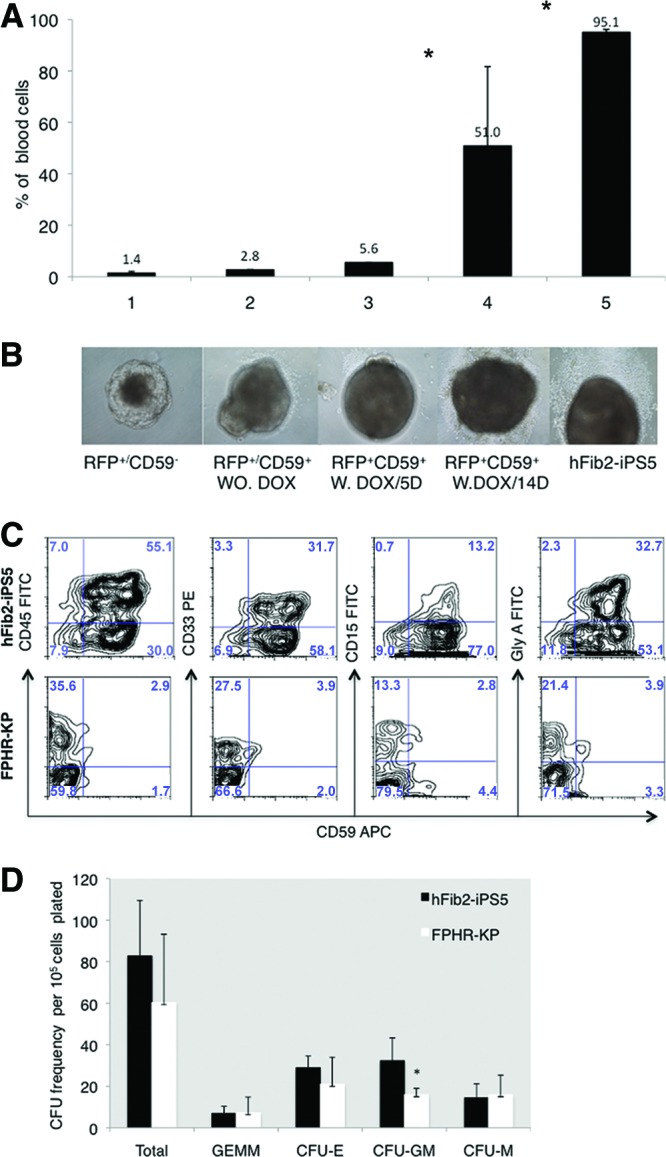
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein (GPI-AP) deficiency beyond the embryoid body (EB) stage does not interfere with hematopoietic differentiation. The FPHR-KP cell line was established by cotransduction with both the PIG-A expression vector and the tetracycline transcriptional suppressor/RFP (regulator). For doxycycline induction, FPHR-KP cells were cultured in human embryonic stem cell medium and exposed to doxycycline for 6 days. Following 6 days of doxycycline treatment, both positive cells for CD59+ and RFP+ were sorted for hematopoietic lineage differentiation markers, and CD59− and RFP+ cells were used as negative and positive controls, respectively. During EB generation, the cells sorted were cultured either with or without doxycycline. (A): After 14 days of EB formation, blood cells appeared, and the percentages of EB-containing blood cells were counted and normalized to a standard number (100 EBs) for each cell line based on three experiments. The percentage of EBs with blood cells in FPHR-KP was higher after 14 days of coculture with doxycycline compared with 5 days of doxycycline treatment and lower than hFib2-iPS5 cells. Significance (*, p < .05) should be between doxycycline 5 days (bar 3) and 14 days (bar 4); significance (*, p < .05) should be between doxycycline 14 days (bar 4) and hFib2-iPS5 (bar 5). (B): Photomicrographs of representative day 14 EBs are shown below each cell subset. Magnification, ×10. (C): Phenotype analysis of the cells derived from hFib2-iPS5 and FPHR-KP EBs. Plots are shown for CD45-FITC/CD59APC, CD33PE/CD59APC, CD15-FITC/CD59APC, and GlyA-FITC/CD59APC in hFib2-iPS5 (top) and FPHR-KP (bottom). (D): Quantitative CFU frequency from hFib2-iPS5 and FPHR-KP cells. Error bars represent SD based on three experiments. There was no significant difference in total CFU colonies between hFib2-iPS5 and FPHR-KP (p > .05), but the number of CFU-GM colonies in hFib2-iPS5 was significantly higher than in FPHR-KP (p < .05). Abbreviations: APC, allophycocyanin; CFU, colony-forming unit; CFU-E, colony-forming unit-erythroid; CFU-GM, colony-forming unit-granulocyte-macrophage; CFU-M, colony-forming unit-macrophage; DOX, doxycycline; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; iPS, induced pluripotent stem cell; PE, phycoerythrin; RFP, red fluorescent probe; W, with; WO, without.
