Figure 7.
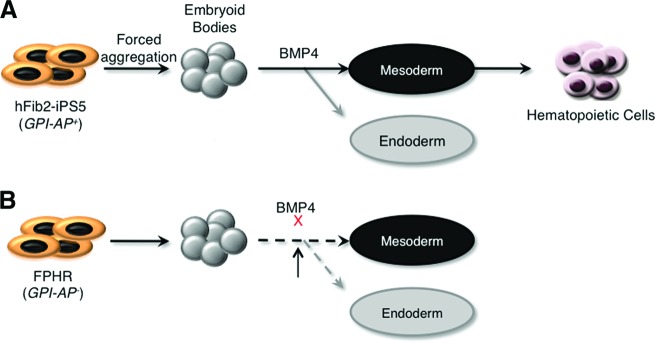
Model of GPI-AP function during embryonic stem (ES)/iPS cell differentiation. (A): In the presence of GPI-APs, ES/iPS cells can form embryoid bodies and then be induced to differentiate into the three germ layers (mesoderm, endoderm, and ectoderm). In the presence of BMP-4, cells are induced toward the mesoderm and endoderm lineages, whereas induction toward the ectoderm lineage is blocked. In the presence of additional cytokines, mesodermal cells can be further differentiated into hematopoietic cells. (B): In the absence of GPI-APs, ES/iPS cells can form embryoid bodies (though abnormal). However, they are unable to be induced to differentiate into either mesoderm or endoderm, likely because of a decrease in BMP-4 signaling activation. Abbreviations: BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; GPI-AP, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein; iPS, induced pluripotent stem cell.
