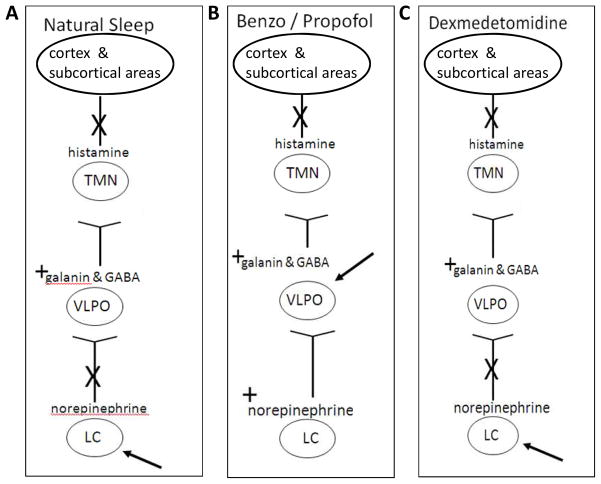
Figure 2. The neuronal pathways of natural sleep, GABA agonists, and dexmedetomidine.
A, In natural sleep, norepinephrine release from the LC is inhibited and this leads to a release of the sleep promoting neurotransmitters, GABA and galanin from the VLPO which then inhibits the release of histamine from the TMN leading to a decrease in consciousness. B, The GABA agonist sedatives interact with the sleep pathway downstream at the level of the VLPO and therefore norepinephrine release from the LC is not inhibited. C, Dexmedetomidine interacts at the level of the LC, and like in natural sleep, the release of norepinephrine from the LC is inhibited.
Definition of abbreviations: LC = locus coeruleus, GABA = γ-aminobutyric acid, VLPO = ventrolateral preoptic nucleus, TMN = tuberomammillary nucleus