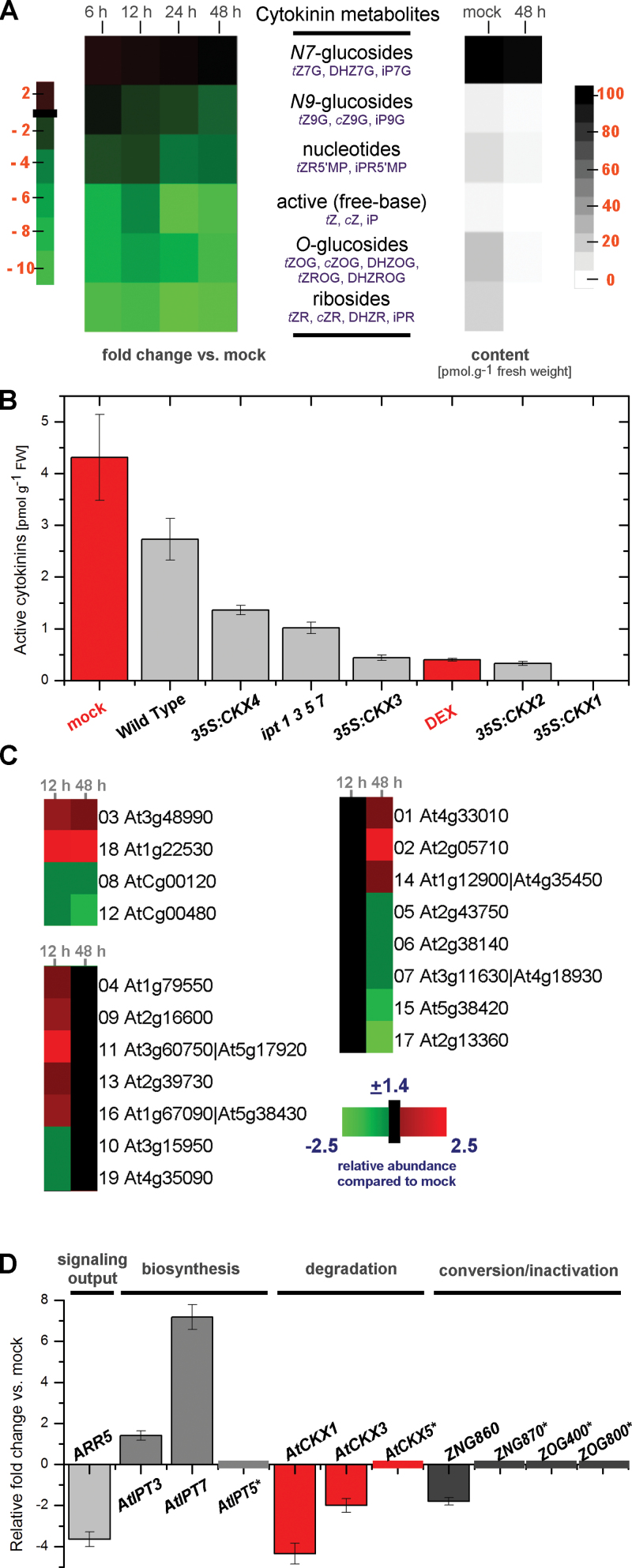
Fig. 1.
DEX-inducible HvCKX2 expression. (A) Time course of cytokinin depletion in CaMV35S>GR>HvCKX2 seedlings following HvCKX2 activation. Seven-day-old seedlings were transferred onto MS medium supplemented with DEX or mock and samples were collected for cytokinin determination 6, 12, 24, and 48h later. (B) Comparison of CK depletion in CaMV35S>GR>HvCKX2 and constitutive 35S:AtCKX transgenics, and the quadruple atipt1 3 5 7 mutant. Pool of active (free base) CKs; data for the CaMV35S>GR>HvCKX2 line (mock, DEX) are marked in red. Data for the 35S:CKX1-35S:CKX4 and ipt1 3 5 7 mutant used in this comparison are from 10-day-old Arabidopsis seedlings as reported by Nishiyama et al. (2011). (C) Proteins that responded to HvCKX2 activation identified by 2-DE analysis. MALDI TOF/TOF MS was used to identify proteins in spots representing differentially regulated proteins at each of the time points. Time courses of changes in their abundance are presented as a heatmap; accession numbers are as in the TAIR database. Numbers correspond to the spot number as given in Supplementary Table S1 at JXB online and in the 2-DE RuBisCO-depleted proteome map (Supplementary Fig. S5). See the Supplementary data for details. (D) Relative fold change in transcripts of 10 genes involved in CK metabolism and signalling by RT–qPCR 48h after HvCKX2 activation.