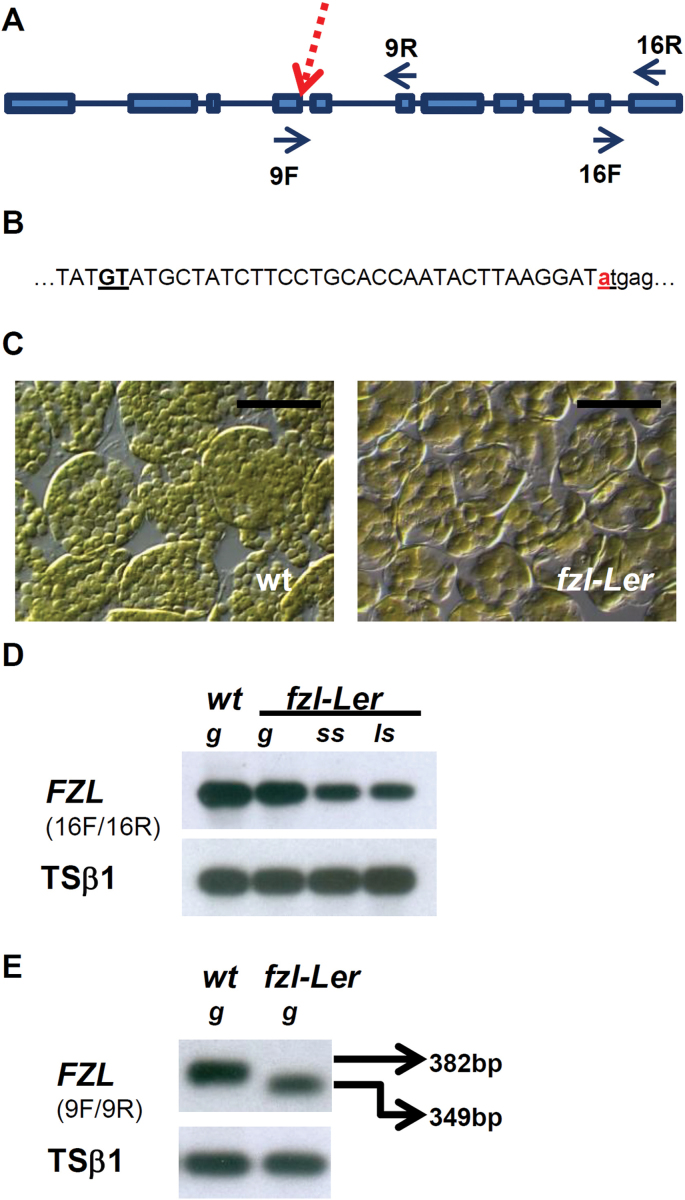
Fig. 2.
Molecular characterization of the fzl-Ler mutation. (A) Schematic representation of the FZL gene. Boxes indicate exons, lines indicate introns, the dotted arrow indicates the site of fzl-Ler mutation (first base of fourth intron), and arrows indicate the positions of the primers used for the RT–PCR analysis represented in D (primers 16F/16R) and E (primers 9F/9R). (B) Partial genomic sequence of the fourth exon (upper case letters) and fourth intron (lower case letters): the mutated base (a instead of the wild-type g) is indicated in red, and the activated cryptic site is underlined. (C) Chloroplast morphology of mesophyll cells of 3-week-old wild-type and fzl-Ler plant leaves. Bars=50 µm. (D) RT–PCR analysis of FZL gene expression in wild-type and fzl-Ler plants, using the primers FZL-16F/16R. (E) Analysis by RT–PCR of splicing of the fourth intron. Using the primers 9F/9R, a PCR product from the wild-type allele of 382bp is amplified and then sequenced, while from the fzl-Ler allele a PCR product of 349bp is amplified and then sequenced. g, green leaves; ss, leaves with small chlorotic spots; ls, leaves with large chlorotic spots.