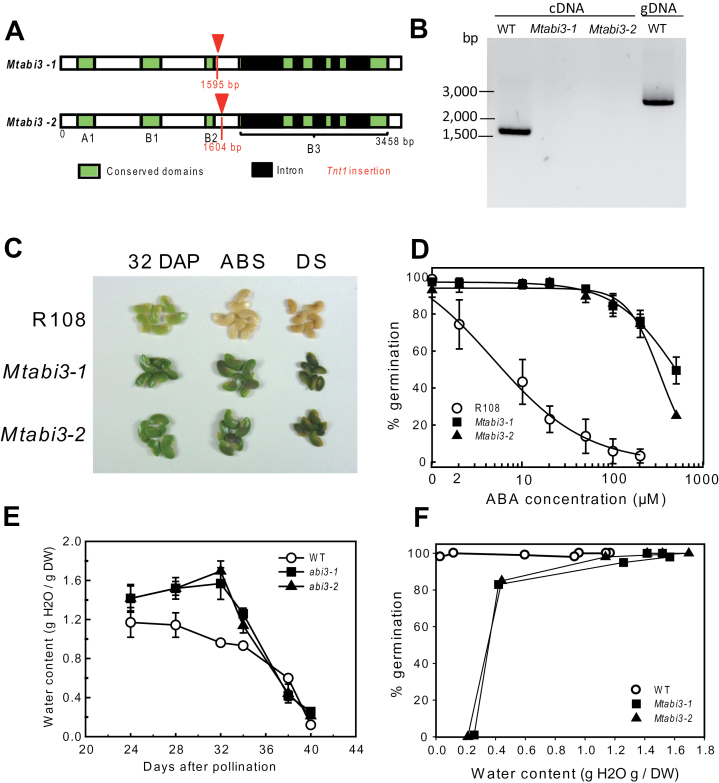
Fig. 5.
Characterization of abscisic acid insensitive3 (Mtabi3) mutants of Medicago truncatula. (A) Gene structure, and position of the A and B domains and Tnt1 insertions within the MtABI3 gene. (B) Validation of the absence of ABI3 transcripts in the Mtabi3-1 and Mtabi3-2 mutants. Using the same primer set, ABI3 was also amplified on genomic DNA. The increased size corresponds to the additional introns. (C) Seed colour phenotype of Mtabi3-1 and Mtabi3-2 and corresponding wild-type seeds (R108) at three stages of maturation: 32 days after pollination (DAP), at pod abscission (ABS, 38 DAP), and in dry seed (DS). (D) ABA dose–response analysis during germination of seeds collected at pod abscission. Germination was scored as emergence of the radicle. Data are the average of three replicates of 40–50 seeds ±SE. (E) Changes in seed water content during development. Data are the average of three replicates of three seeds ±SE. (F) Germination of Mtabi3 and wild-type seeds at different stages of development upon rehydration of 70–80 seeds. Data are significantly different when they differ by ≥18% (χ2 test, P < 0.05).