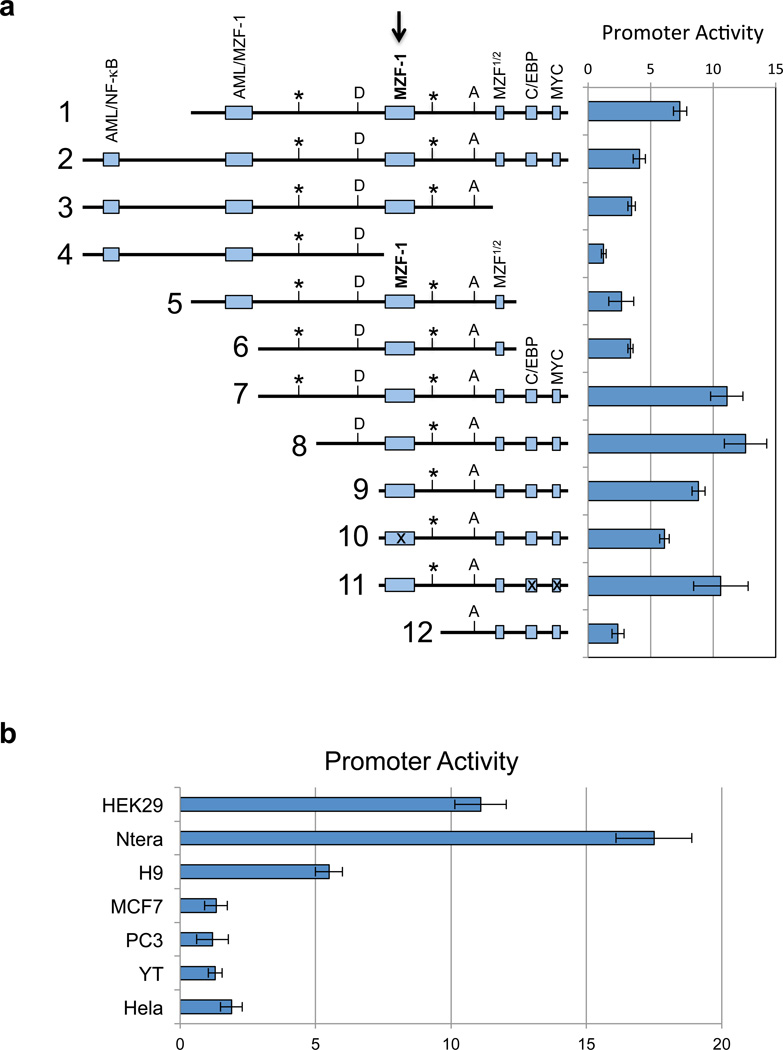
Figure 2.
In vitro analysis of the KIR distal antisense promoter. (a) The left panel is a schematic representation of KIR2DL1 intron 2 fragments shown in an antisense orientation. Potential transcription factor binding sites are indicated by the labeled shaded rectangles. The central MZF-1 site is indicated by the bold arrow. Rectangles containing an “x” represent constructs wherein the respective site has been mutated. The position of the KIR2DL1 and KIR3DL1 distal antisense transcription start sites are indicated by vertical lines labeled with an asterisk. The MYC-binding site indicated at the 3’ end of the distal antisense promoter region overlaps with the exon 2/intron 2 junction on the sense strand. The boundaries of the first KIR2DL1 antisense intron are indicated by vertical lines labeled D (splice donor) and A (splice acceptor). The right panel shows the luciferase activity of pGL3 constructs containing the fragments depicted on the left. Constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells and relative luciferase activity was determined 48 hours post-transfection. Values represent the mean, and error bars indicate the standard deviation of at least 3 independent experiments. (b) Analysis of KIR2DL1 distal promoter activity (construct 7 in a) in various cell lines is shown. Values represent the mean and error bars indicate the standard deviation of at least 3 independent experiments.