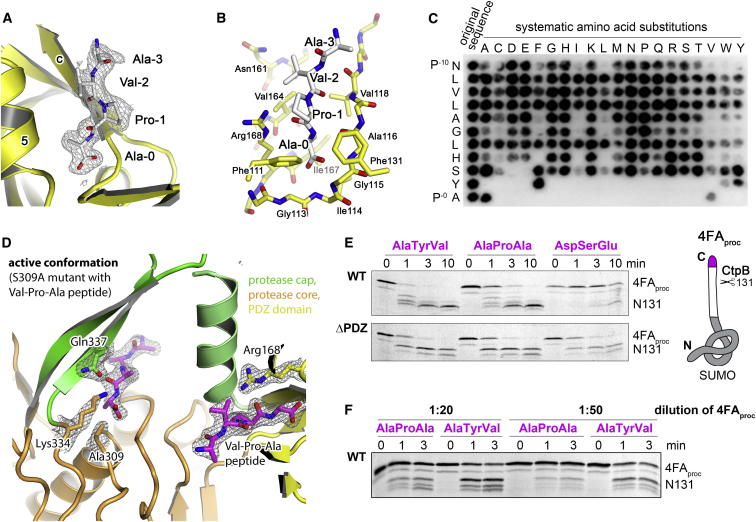
Figure 4.
Peptide Binding to the PDZ Domain Regulates CtpB Activity
(A) Omit electron density of a cocrystallized peptide bound to the PDZ domain (1.9 Å resolution, contoured at 1.2 σ).
(B) Detailed presentation of the substrate-binding pocket of the PDZ domain with bound peptide ligand (white). Residues involved in peptide binding are shown in stick presentation and are labeled.
(C) Secondary peptide spot screen of an identified PDZ binder (NH2-NLVLAGLHSYA-COOH, spot 594 in Figure S4A). As indicated, amino acids were systematically varied.
(D) Ribbon plot of the proteolytically impaired S309A (colored according to domains) that was cocrystallized with the NH2-EMDKPQTAAVPA-COOH peptide in the active conformation. Peptides bound to the proteolytic site and PDZ domain (stereoview in Figure S4D) and selected CtpB residues are shown in stick mode and are overlaid with the corresponding 2Fo-Fc omit electron density (1.9 Å resolution, contoured at 1.2 σ).
(E) Cleavage assays of in vitro translated 4FAproc constructs carrying distinct C termini. Substrates and products are visualized by 35S-methionine autoradiography and are labeled.
(F) Cleavage assays of 4FAproc constructs that were applied at decreasing concentrations. See also Figure S4 and Table S2.