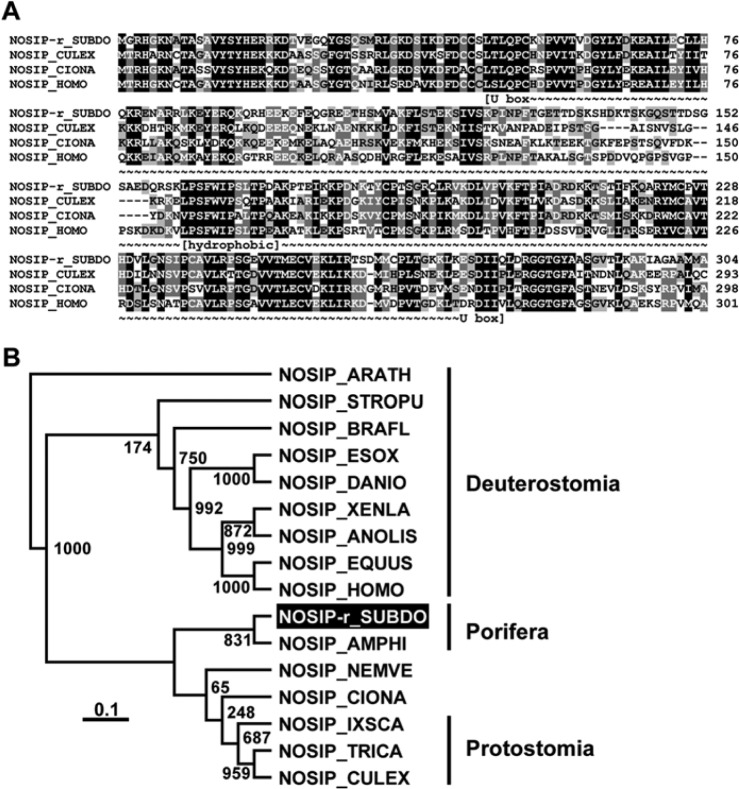
Figure 5.
The Suberites domuncula nitric oxide synthase–interacting protein (NOSIP) (NOSIP-r_SUBDO). (A) The deduced sponge NOSIP is aligned with related sequences from Culex quinquefasciatus (NOSIP_CULEX; accession number XP_001865022.1), Ciona intestinalis (NOSIP_CIONA; XP_002122091.1), and human (NOSIP_HOMO; NP_057037.1). The U box consensus (~~~) and the predicted membrane docking segment of the protein (hydrophobic) are marked. Residues conserved (similar or related with respect to their physicochemical properties) in all sequences are shown in white on black, and those in at least three sequences in black on gray. (B) These four sequences are compared with the related sequences from Equus caballus (NOSIP_EQUUS; XP_001492183.1), the bird Anolis carolinensis (NOSIP _ANOLIS; XP_003222746.1), the fishes Esox lucius (NOSIP_ESOX; ACO13473.1), and Danio rerio (NOSIP_DANIO; NP_001007435.1), as well as to NOSIP from Xenopus laevis (NOSIP_XENLA; NP_001084604.1), then Branchiostoma floridae (NOSIP_BRAFL; XP_002608258.1) and Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (NOSIP_STROPU; XP_790354.2), the insects Ixodes scapularis (NOSIP_IXSCA; XP_002434038.1) and Tribolium castaneum (NOSIP_TRICA; XP_966634.1), and the sequences from Nematostella vectensis (NOSIP_NEMVE; XP_001632123.1) and Amphimedon queenslandica (NOSIP_AMPHI; XP_003385646.1). The plant sequence from Arabidopsis thaliana (NOSIP_ARATH; NP_564781.1) was used as an out-group to root the tree. The scale bar indicates an evolutionary distance of 0.1 amino acid substitutions per position in the sequence.