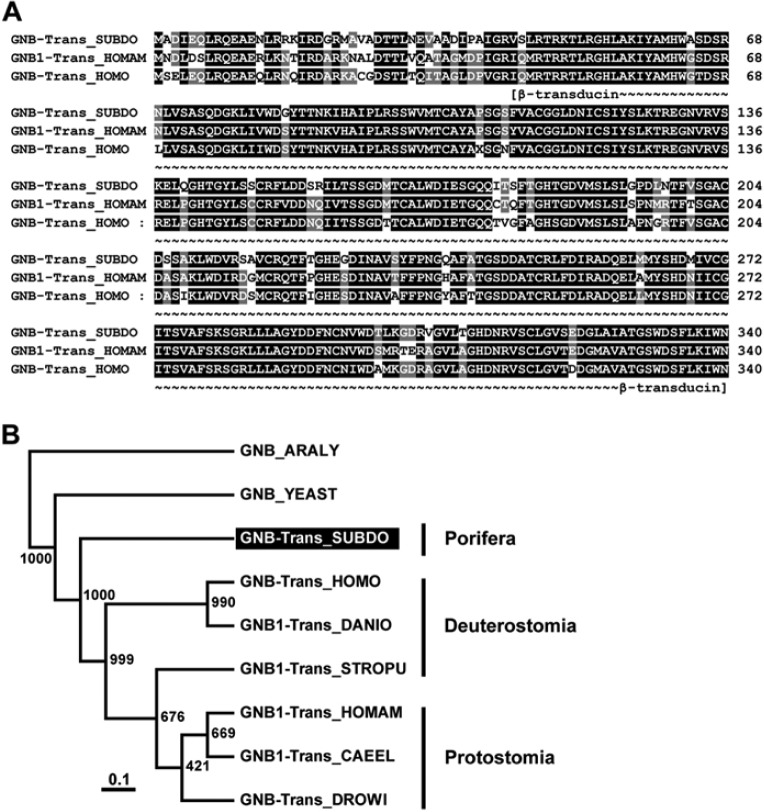
Figure 6.
The Suberites domuncula putative transducin β subunit (GNB-trans_SUBDO). (A) The deduced sponge polypeptide GNB-Trans_SUBDO was aligned with the related Gβ-subunit from human (GNB-Trans_HOMO; AAA35922.1) and the American lobster Homarus americanus (GNB1-Trans_HOMAM; O45040.1). Residues conserved (identical or similar with respect to their physicochemical properties) in all three sequences are shown in white on black; those that share similarity to at least two residues are shown in white on gray. The regions spanning the β-transducin repeats (β-transducin) are marked. (B) These three proteins were compared with the related Gβ-subunits from the fish Danio rerio (GNB1-Trans_DANIO; NP_997774), insect Drosophila willistoni (GNB-Trans_DROWI; XP_002075419.1), nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (GNB1-Trans_CAEEL; NP_001254312.1), sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (GNB1-Trans_STROPU; XP_001176793.1), and yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae (GNB_YEAST; AAA35114.1). The protein, from the plant Arabidopsis lyrata (GNB_ARALY; XP_002867119.1), was used as an out-group to root the tree. Scale bar indicates an evolutionary distance of 0.1 amino acid substitutions per position in the sequence.