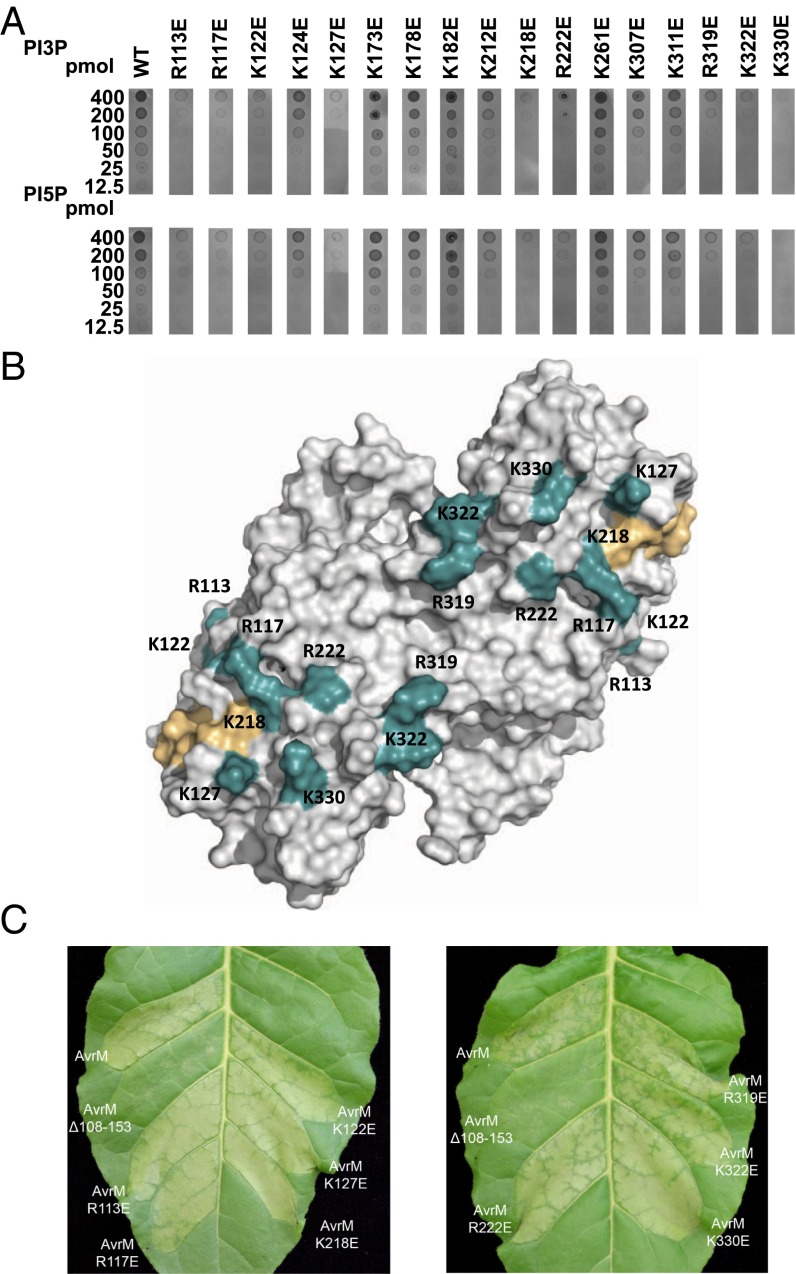
Fig. 4.
PIP binding to AvrM is charge-dependent and is not required for uptake. (A) Protein-lipid overlay assay of Escherichia coli-expressed GST-AvrM-A and single Glu substitutions of surface exposed Arg and Lys residues. Serial dilutions (400, 200, 100, 50, 25, and 12.5 pmol) of PI3P and PI5P were spotted onto nitrocellulose membranes and incubated with WT or mutant AvrM-A. After rigorous washing, bound proteins were detected by using anti-GST/alkaline phosphatase antibodies. (B) Positions of the reverse-charge mutants (teal) that reduced or abrogated PIP binding (R113E, R117E, K122E, K127E, K218E, R222E, R319E, K322E, and K330E) on the structure of the AvrM-A dimer. The conserved surface patch important for AvrM internalization is shown in light orange. (C) Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of AvrM-A, AvrM-A with an internal deletion of amino acids 108 to 153 and AvrM-A mutants (shown in B) in leaves of transgenic tobacco plants (W38) containing the M resistance gene. All the AvrM constructs included the 28-aa signal peptide and a C-terminal citrine domain. Agroinfiltrations were performed at an OD600 of 0.4, and images were prepared 29 hpi.