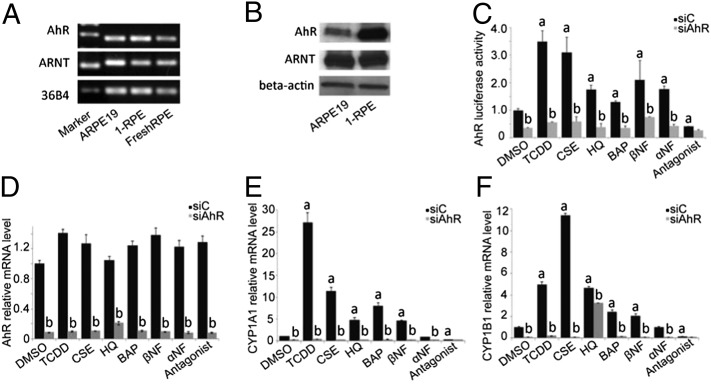
Fig. 1.
AhR signaling pathway is active in human RPE cells. Each in vitro experiment was performed a minimum of three times. Data are means ± SEM for all graphs. a, Significantly different relative to DMSO treated cells (P < 0.05); b, significantly different relative to drug-SiC-–treated cells (P < 0.05). ARPE19 cell culture: 1-RPE, primary RPE cell culture, and FreshRPE, freshly harvested human RPE, express AhR and ARNT (A) mRNA and (B) protein. (C) AhR activity in ARPE19 cells following transfection with AhR-tk-luciferase reporter. Cells were treated with known agonists [10 nM TCDD, 1.50% cigarette smoke extract-CSE, 75 μM hydroquinone-HQ, 1 μM benzo(a)pyrene-BAP, 100 nM β-napthoflavone-βNF, 100 nM α-napthoflavone-αNF] and 1 μM AhR antagonist (Calbiochem182705) for the receptor for 24 h, with siRNA knockdown of the AhR or scrambled siRNA control (siC). (D) Using qPCR, decreased AhR mRNA was observed in ARPE19 cells following siRNA knockdown (gray bars) compared with scrambled siRNA control (black bars). mRNA expression of known AhR target genes (E) CYP1A1 and (F) CYP1B1 in ARPE19 cells treated with AhR agonists and an antagonist, for 24 h, with and without siRNA knockdown.