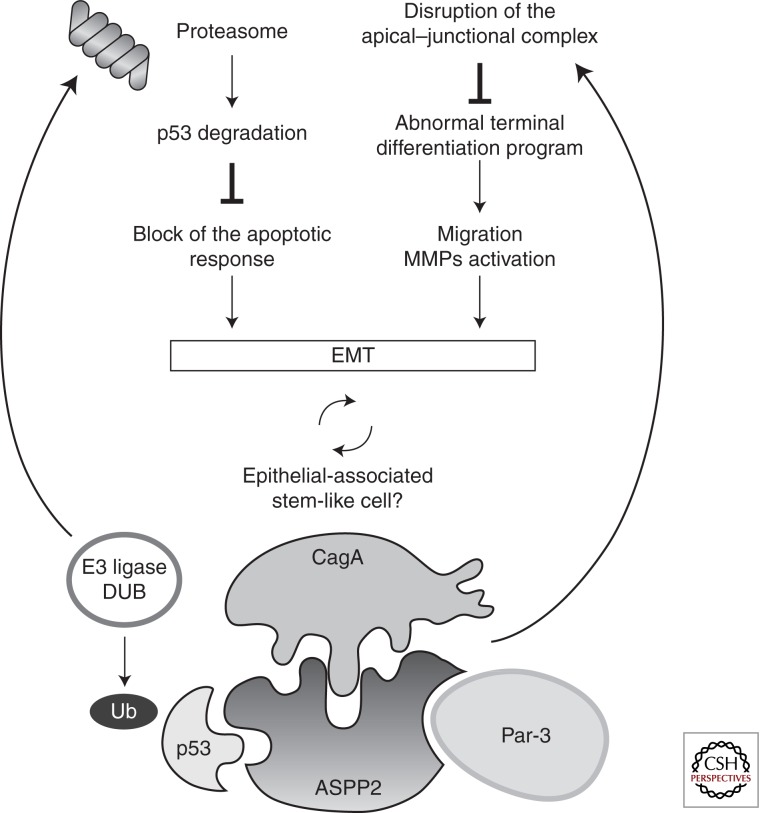
Figure 3.
Schematic model of the effects induced by the CagA-ASPP2 interaction. CagA binds ASPP2, and this complex is responsible for proteasome-dependent p53 degradation. Cells harboring CagA are unable to cause apoptosis. In addition, they acquire the ability to migrate, invade, and they lack a terminal differentiation program (EMT).