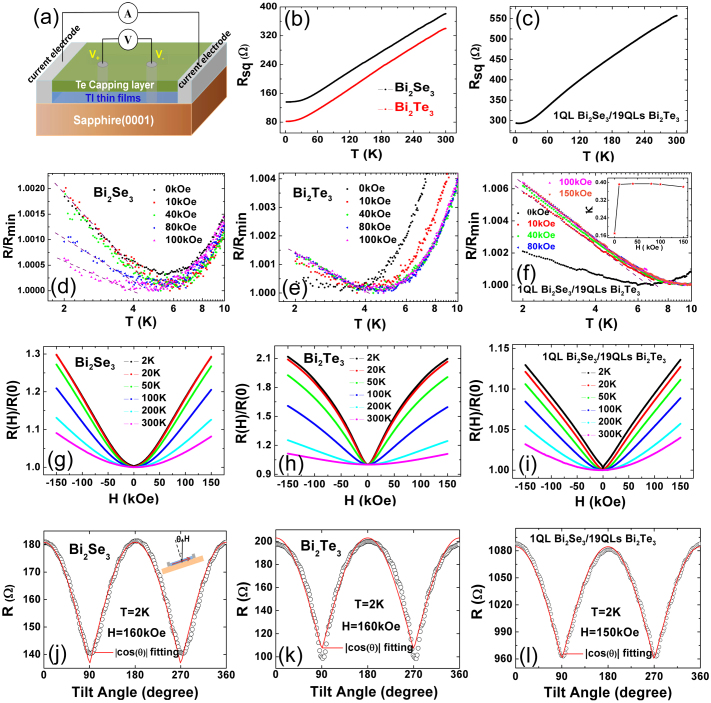
Figure 3. Transport measurements on 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 heterosturcture films.
(a) Schematic structure of the TI films for transport measurements. The thickness is not to scale. (b) 2D sheet resistance (Rsq) vs temperature of 20 QLs Bi2Se3 and 20 QLs Bi2Te3 from room temperature to 2 K. (c) 2D sheet resistance (Rsq) as a function of temperature for 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 heterostructure film. (d)–(f) The normalized resistance (R/Rmin) of 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 as a function of temperature at different magnetic field, indicate that a logarithmic increase with decreasing T (the dashed lines are guides to the eyes). In the upper inset of (f), the slope defined as κ = (πh/e2)dσxx/dlnΤ is shown as a function of magnetic field. (g)–(i) The normalized MR (R(H)/R(0)) vs magnetic field of 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 at different temperatures. (j) and (k) Resistance vs tilt angle of 20 QLs Bi2Se3 and 20 QLs Bi2Te3 in a fixed magnetic field of 160 kOe at T = 2 K. The inset shows the rotation configuration. The magnetic field is always perpendicular to the current when the sample is rotating. (l) Resistance vs tilt angle of 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 in a fixed magnetic field of 150 kOe at T = 2 K. The function |cosθ| fitting is shown as solid red lines in (j)–(l).