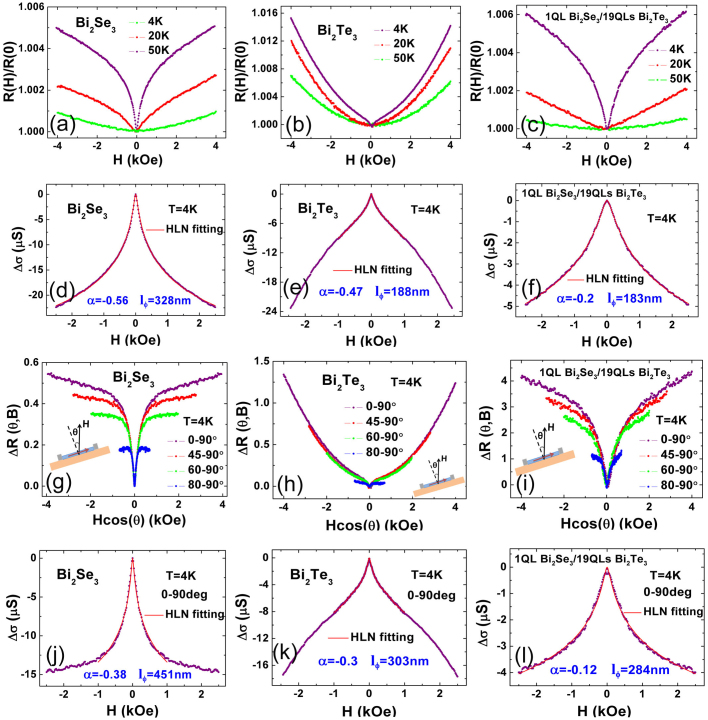
Figure 4. WAL effect studied on 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 films.
(a)–(c) Normalized MR of 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 in the low field at different temperatures. (d)–(f) Fitted curves (solid red lines) with Eq. (1) are shown in 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 in perpendicular field at T = 4 K respectively. For the 20 QLs Bi2Se3 film and the 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 film, the fitting range is from 2.5 kOe to −2.5 kOe. However, for the 20 QLs Bi2Te3 film, the WAL dip is small that the fitting range is from 1 kOe to −1 kOe. (g)–(i) MR as a function of the normal H component with the θ = 90° MR subtracted for 20 QLs Bi2Se3, 20 QLs Bi2Te3 and 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Se3 at θ equals to 0°, 45°, 60°, 80°. The inset shows the rotation configuration. (j)–(l) Violet symbols are the T = 4 K magneto conductance for the 20 QLs Bi2Se3 film (j), the 20 QLs Bi2Te3 film (k) and the 1 QL Bi2Se3/19 QLs Bi2Te3 film (l) after subtracting the 3D WAL effect. The solid red lines show the fitting results with Eq. (1). Compared with corresponding figure (d) to (f), all the phase coherence lengths of our TI films become larger after subtracting the 3D WAL effect.